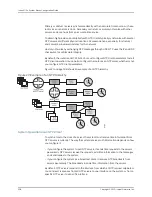
•
Peer—IP address of server, status of the server: configured, master, selected,
candidate, correct, or unusable
•
configured—Confirmation that you assigned this NTP server to the system
•
master
—
System has chosen this server as the master
•
selected
—
System will consider this server when it chooses the master
•
candidate
—
System may consider this server when it chooses the master
•
correct—System considers the server’s clock to be reasonably correct
•
unusable
—
Server does not meet the initial criteria for the master
•
stratum—Number of hops between the server and its stratum 1 server
•
Peer is a Broadcast/Configured Server—Type of NTP server: one that broadcasts
NTP messages or one you have configured for NTP services
•
version—Version of NTP on the server
•
polled every—Time between NTP requests from the system to the server
•
polls every—Time between NTP requests from the server to its NTP servers
•
Root Delay—Round-trip time between the server and its stratum 1 root server
•
Root Dispersion—Measure of all the errors associated with the network hops and
servers between the server and its stratum 1 server
•
Sync Dist.—Measure of the total time error since the update in the path to the
stratum 1 server
•
Peer Delay—Round-trip delay, with the lowest dispersion value in the sample
buffer, between the system and the server
•
Peer Dispersion—Lowest measure, in the sample buffer, of the error associated
with the peer offset, based on the peer delay and precision
•
Offset—Difference, with the lowest dispersion in the sample buffer, between the
system’s clock and the server’s clock
•
Reachability
—
8-bit number that shows whether or not the NTP server responded
to the last eight requests from the system; one indicates a response; zero indicates
no response. For example, 11111111 indicates that the NTP server responded to the
last eight requests. If the system reaches one server less often than it does other
servers, that server is not a good choice for the master.
•
Precision—Length of the clock tick (interrupt interval) of the server’s clock
•
Source—IP address of the interface to which NTP servers should send NTP
responses
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
520
JunosE 11.3.x System Basics Configuration Guide
Summary of Contents for JUNOSE 11.3
Page 6: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc vi...
Page 8: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc viii JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 24: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc xxiv JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 32: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 2 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 146: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 116 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 166: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 136 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 432: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 402 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 488: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 458 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 524: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 494 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 554: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 524 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 566: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 536 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 588: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 558 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 613: ...PART 3 Index Index on page 585 583 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc...
Page 614: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 584 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 632: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 602 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...