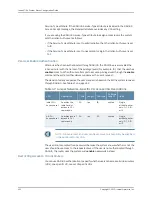
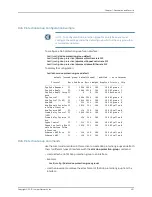
When a distributed DoS attack occurs on a line module, suspicious flow control resources
can be exhausted. To provide further counter measures, you can enable the group feature,
where flows are grouped together and treated as a whole. If you do not use the group
feature, suspicious flows can fill up the suspicious flow table and prevent detection of
additional attacking flows.
Suspicious Control Flow Monitoring
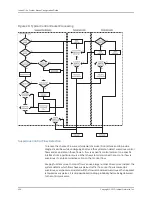
Each protocol has a per-protocol rate limit. The rate limiter is used to limit the rate of
packets that proceed to the control processor for the specific protocol. Per-protocol rate
limiting is also used to begin the process by which flows of the specific protocol are
monitored.
Each priority has a per-priority rate limit. The rate limiter limits the rate of packets that
proceed to the control processor for the specific priority. It also begins the process by
which flows of the specific priority are monitored.
All protocols on each line module have a rate limit. Each protocol is associated with a
given priority, which is also provided with a rate limit. When a slot comes under attack,
the first lines of defense are the protocol and priority rate limiters. If the line module
determines that a specific protocol or priority is under attack (because the rate has been
exceeded), it proceeds to monitor all flows from the problem protocol or priority. Initially,
a control flow is marked as nonsuspicious.
After a control flow is placed in the suspicious flow table, the system inspects all packets
that belong to the flow. The interface controller (IC) and forwarding controller (FC)
monitor the table to determine whether the suspicious flow has a packet rate above the
suspicious level. If the packet rate is above this level, the flow is marked as suspicious.
Marking a control flow as suspicious affects only a particular protocol on a particular
interface. When a flow is marked as suspicious, all packets belonging to that flow are
marked as suspicious and trapped at the forwarding controller.
Suspicious control flows are continually monitored. The flow can be restored if the flow
goes below the low threshold level. The flow can also be restored based on a backoff
timer. The flow is removed from the suspicious flow table if the related interface is
removed.
Approximately 2000 flows can be monitored as suspicious at any time for each line
module. When the suspicious flow table on a particular line module reaches its maximum
and the system is not set to group flows, flows that should be marked as suspicious
proceed as nonsuspicious. When you return a suspicious flow to a nonsuspicious state
or delete it, the flows that did not fit into the table are added to the table.
By default, the system groups flows when the suspicious flow table size is exceeded on
a line module. When the flow table is full, instead of marking a specific flow in that group
as suspicious and providing information on each flow on that line module, the system
groups flows based on group membership and provides information on the group instead
of each flow. This flow information is useful under severe distributed DoS attacks. Group
membership is based on physical port and control protocol; all flows in that group are
considered suspicious.
437
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 7: Passwords and Security
Summary of Contents for JUNOSE 11.3
Page 6: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc vi...
Page 8: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc viii JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 24: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc xxiv JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 32: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 2 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 146: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 116 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 166: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 136 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 432: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 402 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 488: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 458 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 524: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 494 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 554: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 524 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 566: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 536 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 588: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 558 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 613: ...PART 3 Index Index on page 585 583 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc...
Page 614: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 584 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 632: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 602 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...