3-25
BUS INTERFACE UNIT
The minimum device data hold time (from WR high) is defined by T
DH
. The calculated value
must be greater than the minimum device requirements; however, the value can be changed only
by decreasing the clock rate.
T
WC
and T
WP
define the minimum time (maximum frequency) a device can process write bus cy-
cles. T
WR
determines the minimum time from the end of the current write cycle to the start of the
next write cycle. All three parameters require that calculated values be greater than device re-
quirements. The calculated T
WC
and T
WP
values increase with the insertion of wait states. The cal-
culated T
WR
value, however, can be changed only by decreasing the clock rate.
3.5.3 Interrupt Acknowledge Bus Cycle
Interrupt expansion is accomplished by interfacing the Interrupt Control Unit with a peripheral
device such as the 82C59A Programmable Interrupt Controller. (See Chapter 8, “Interrupt Con-
trol Unit,” for more information.) The BIU controls the bus cycles required to fetch vector infor-
mation from the peripheral device, then passes the information to the CPU. These bus cycles,
collectively known as Interrupt Acknowledge bus cycles, operate similarly to read bus cycles.
However, instead of generating RD to enable the peripheral, the INTA signal is used. Figure 3-23
illustrates a typical Interrupt Acknowledge (or INTA) bus cycle.
An Interrupt Acknowledge bus cycle consists of two consecutive bus cycles. LOCK is generated
to indicate the sequential bus operation. The second bus cycle strobes vector information only
from the lower half of the bus (D7:0). In a 16-bit bus system, the upper half of the bus (D15:8)
floats.
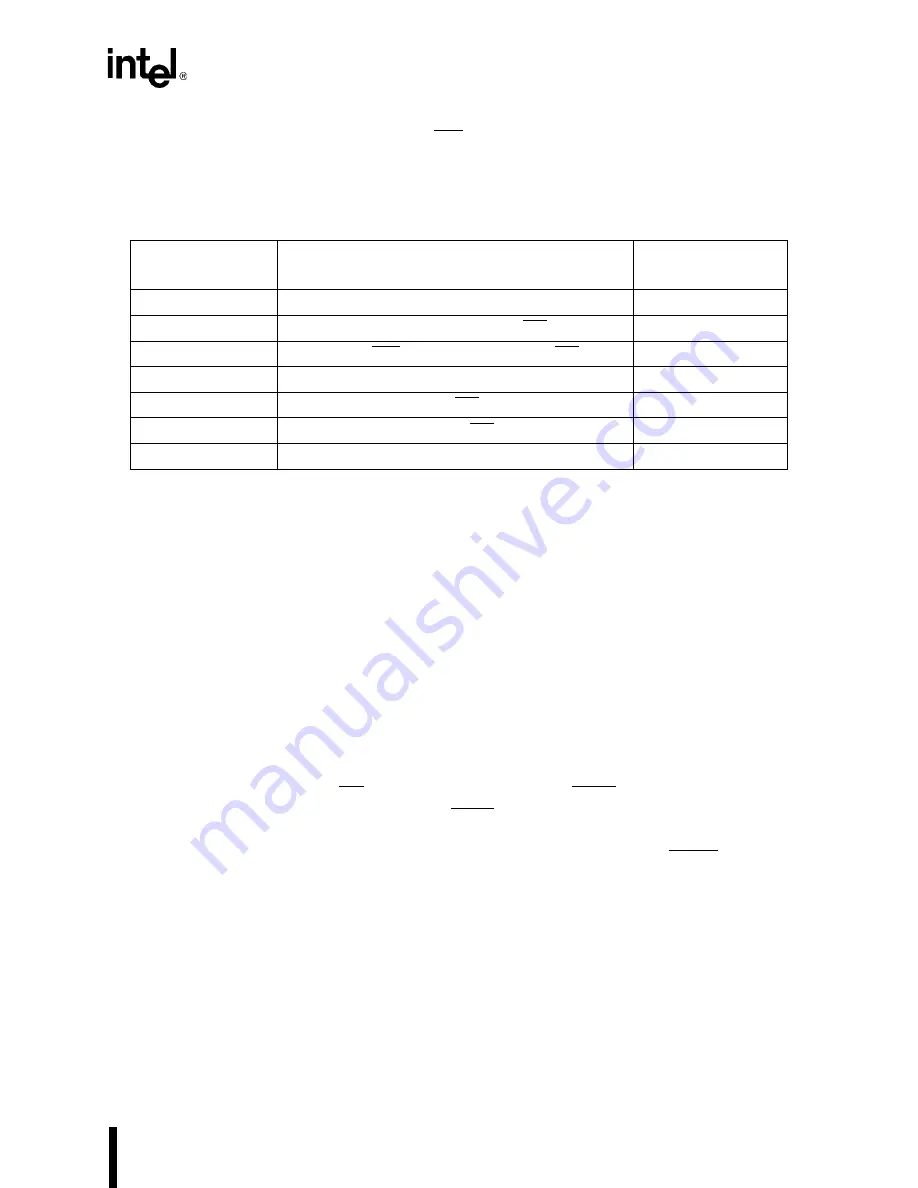
Table 3-5. Write Cycle Critical Timing Parameters
Memory Device
Parameter
Description
Equation
T
WC
Write cycle time
4T
T
AW
Address valid to end of write strobe (WR high)
3T –
T
ADLTCH
T
CW
Chip enable (LCS) to end of write strobe (WR high)
3T
T
WR
Write recover time
T
WHLH
T
DW
Data valid to write strobe (WR high)
2T
T
DH
Data hold from write strobe (WR high)
T
WHDX
T
WP
Write pulse width
T
WLWH
Summary of Contents for 80C186EA
Page 1: ...80C186EA 80C188EA Microprocessor User s Manual...
Page 2: ...80C186EA 80C188EA Microprocessor User s Manual 1995...
Page 19: ......
Page 20: ...1 Introduction...
Page 21: ......
Page 28: ...2 Overview of the 80C186 Family Architecture...
Page 29: ......
Page 79: ......
Page 80: ...3 Bus Interface Unit...
Page 81: ......
Page 129: ......
Page 130: ...4 Peripheral Control Block...
Page 131: ......
Page 139: ......
Page 140: ...5 ClockGenerationand Power Management...
Page 141: ......
Page 165: ......
Page 166: ...6 Chip Select Unit...
Page 167: ......
Page 190: ...7 Refresh Control Unit...
Page 191: ......
Page 205: ......
Page 206: ...8 Interrupt Control Unit...
Page 207: ......
Page 239: ...INTERRUPT CONTROL UNIT 8 32...
Page 240: ...9 Timer Counter Unit...
Page 241: ......
Page 265: ......
Page 266: ...10 Direct Memory Access Unit...
Page 267: ......
Page 295: ...DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS UNIT 10 28...
Page 296: ...11 Math Coprocessing...
Page 297: ......
Page 314: ...12 ONCE Mode...
Page 315: ......
Page 318: ...A 80C186 Instruction Set Additions and Extensions...
Page 319: ......
Page 330: ...B Input Synchronization...
Page 331: ......
Page 334: ...C Instruction Set Descriptions...
Page 335: ......
Page 383: ...INSTRUCTION SET DESCRIPTIONS C 48...
Page 384: ...D Instruction Set Opcodes and Clock Cycles...
Page 385: ......
Page 408: ...Index...
Page 409: ......
















































