November, 2018 Rev.1.4
37
Data Pointer Register (DPTR)
The Data Pointer (DPTR) is a 16-bit register which is used to form 16-
bit addresses for External Data Memory accesses (MOVX A, @DPTR and MOVX @DPTR, A), for
program byte moves (MOVC A, @A+DPTR) and for indirect program jumps (JMP @A+DPTR).
Two true 16-bit operations are allowed on the Data Pointer – load immediate (MOV DPTR, #data) and
increment (INC DPTR).
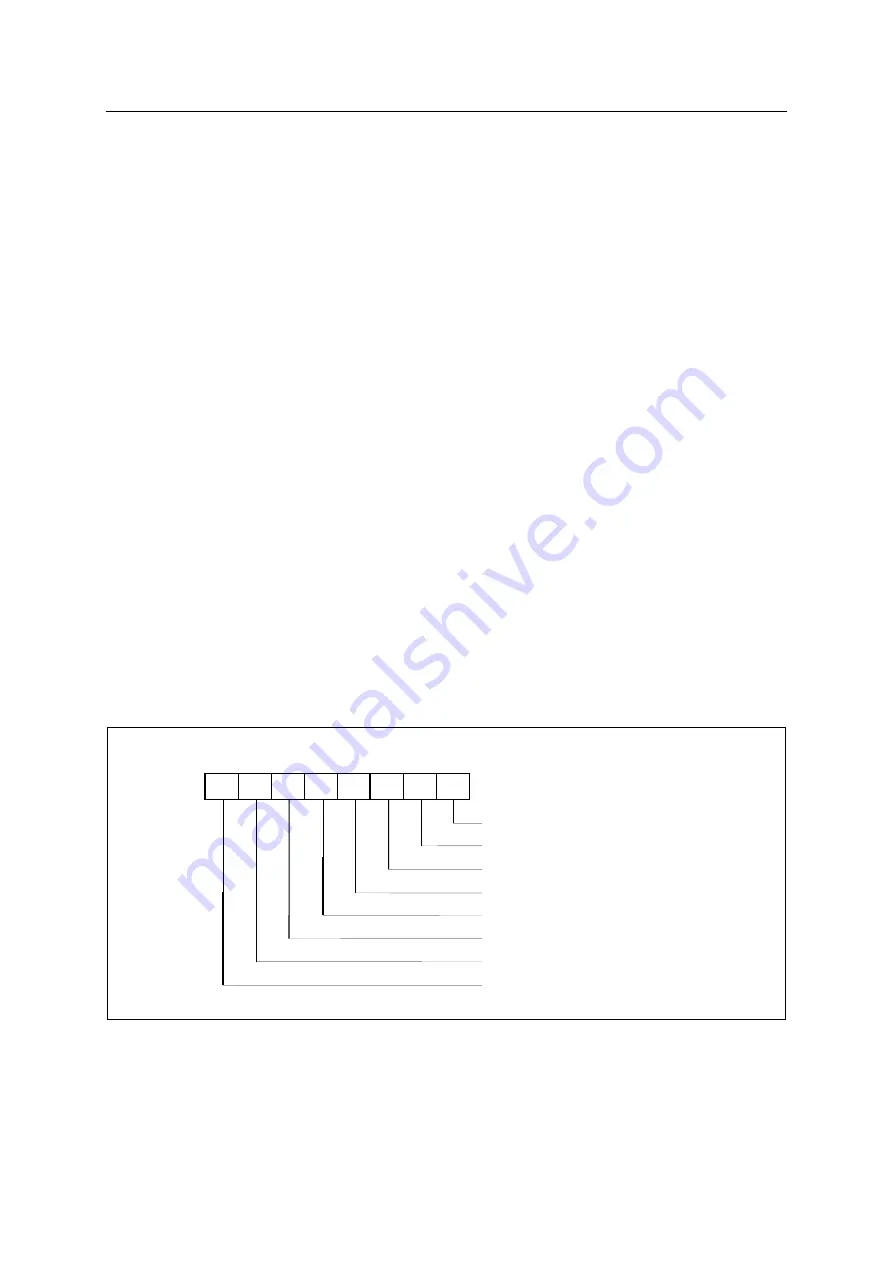
Program Status Word (PSW)
The PSW contains several status bits that reflect the current state of
the CPU. The PSW, shown in Figure 8.1, resides in SFR space. It contains the Carry bit, the Auxiliary
Carry (for BCD operations), the two register bank select bits, the Overflow flag, a Parity bit, and two
user-definable status flags.
CY
The Carry bit, other than serving the function of a Carry bit in arithmetic operations, also serves as
the “Accumulator” for a number of Boolean operations.
AC
The Auxiliary Carry bit, this bit is set when there is a carry from bit 3 of ALU or there is no borrow
from bit 4 of ALU after operation.
RS0, RS1
The bits RS0 and RS1 are used to select one of the four register banks shown in Figure
8.3. A number of instructions refer to these RAM locations as R0 through R7. The selection of which
of the four banks is being referred to is made on the basis of the bits RS0 and RS1 at execution time.
OV
Overflow flag. This bit is set to “1” when an overflow occurs as the result of an arithmetic operation
involving signs. An overflow occurs when the result of an addition or subtraction e127(7F
H
)
or 128(80
H
). The CLRV instruction clears the overflow flag. There is no set instruction. When the BIT
instruction is executed, bit 6 of memory is copied to this flag.
P
The Parity bit reflects the number of 1s in the Accumulator: P=1 if the Accumulator contains an odd
number of 1s, and P=0 if the Accumulator contains an even number of 1s. Thus the number of 1s in
the Accumulator plus P is always even.
Two bits in the PSW are uncommitted and may be used as general purpose status flags.
Program Status Word
Parity Flag
User-definable Flag
ALU overflow Flag
Register Bank Select 0 Flag
Register Bank Select 1 Flag
General Purpose User-definable Flag
ALU Auxilliary Carry Flag
ALU Carry Flag
0
2
4
3
5
6
7
1
RS0 OV
F1
P
CY AC
F0 RS1
Figure 8-4 PSW Register
Summary of Contents for MC96FR364B
Page 17: ...MC96FR364B November 2018 Rev 1 4 17 4 PACKAGE DIMENSION...
Page 18: ...MC96FR364B 18 November 2018 Rev 1 4 Figure 4 1 PKG DIMENSION 28 TSSOP...
Page 23: ...MC96FR364B November 2018 Rev 1 4 23 6 3 REMOUT Port Data PAD VDD Figure 6 3 REMOUT port...
Page 69: ...November 2018 Rev 1 4 69 Initial value 00H BIT 7 0 BIT counter value...
















































