4-14 Troubleshooting and Repair
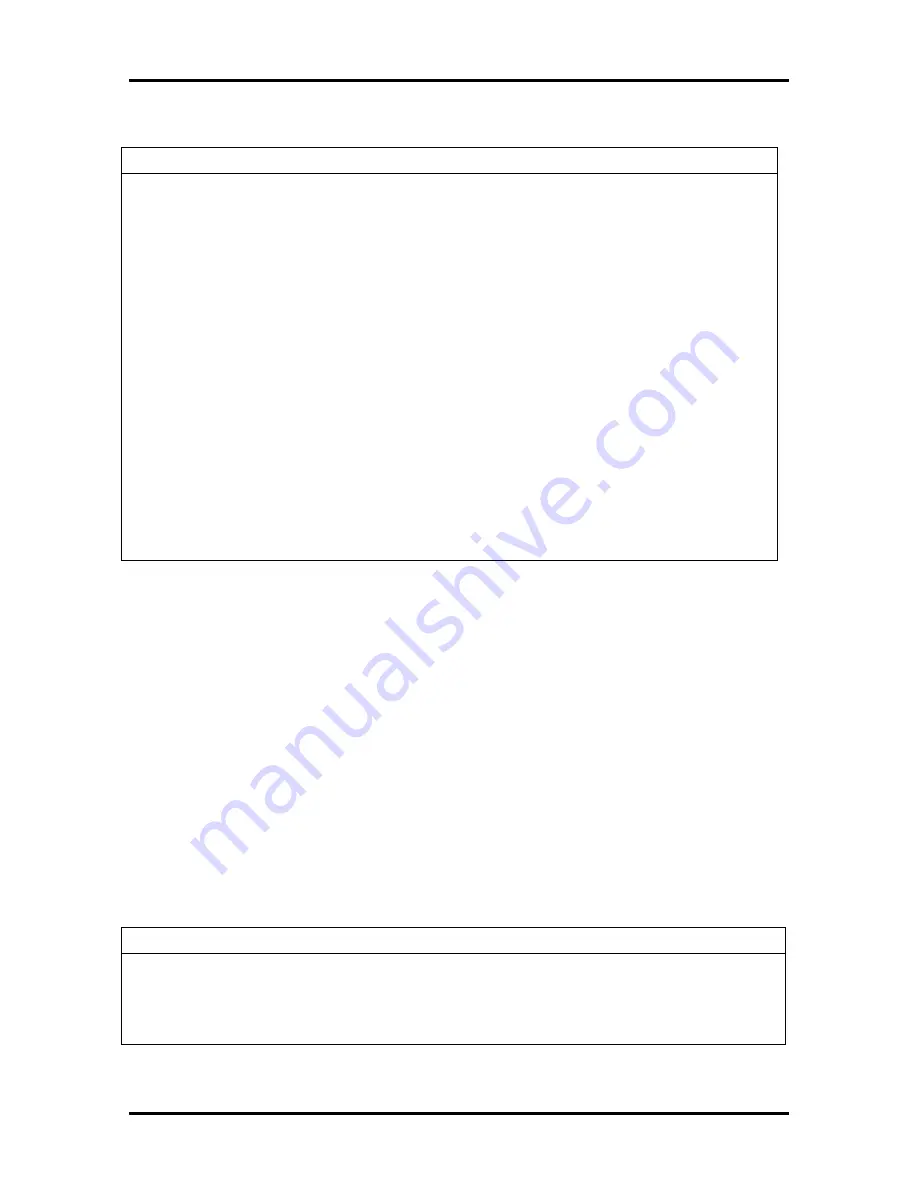
Table Section 4-3 Problems and Solutions
Problem
Symptom
Solution
Keyboard or mouse
malfunction
Monitor has prompt, but cannot
input data.
1
. Check that keyboard/mouse is
plugged in.
2
. Check password utility (see
Section 2).
3
. Disable password utility (see
Section 2).
4
. Replace keyboard (or mouse).
5
. Replace system board.
Communication
error
No or bad data when
communicating.
1
. Check cable connections between
system board and device.
2
. Check that the interface port is
selected.
3
. Test or replace device and interface
cable.
4
. Replace system board.
Diagnostic Output and Beep Codes
One beep indicates that the computer has completed its power-on self-test. If intermittent
beeping occurs, power off the computer and try again. If the beeping persists, see Table
Section 4-5 for diagnostic outputs and beep codes.
The diagnostic port output codes are placed at the diagnostic status port (port 80) to indi-
cate tests in progress and failed tests to someone with hardware that can detect the output.
If the FAILBEEP option is selected, the Beep codes are announced on the speaker only if a
fatal failure is detected. For instance, “2-2-3” (a burst of two beeps, a burst of two beeps, a
burst of three beeps) indicates a failure of the BIOS ROM checksum. Both sets of codes are
only used prior to screen initialization and screen retrace verification. Once the screen is
believed operable, diagnostic reporting is via screen messages.
Table Section 4-5 Diagnostic Output and Beep Codes
Code
Beeps
Description of Test or Failure at POST
02
verify real mode
04
get CPU type
06
initialize system hardware
















































