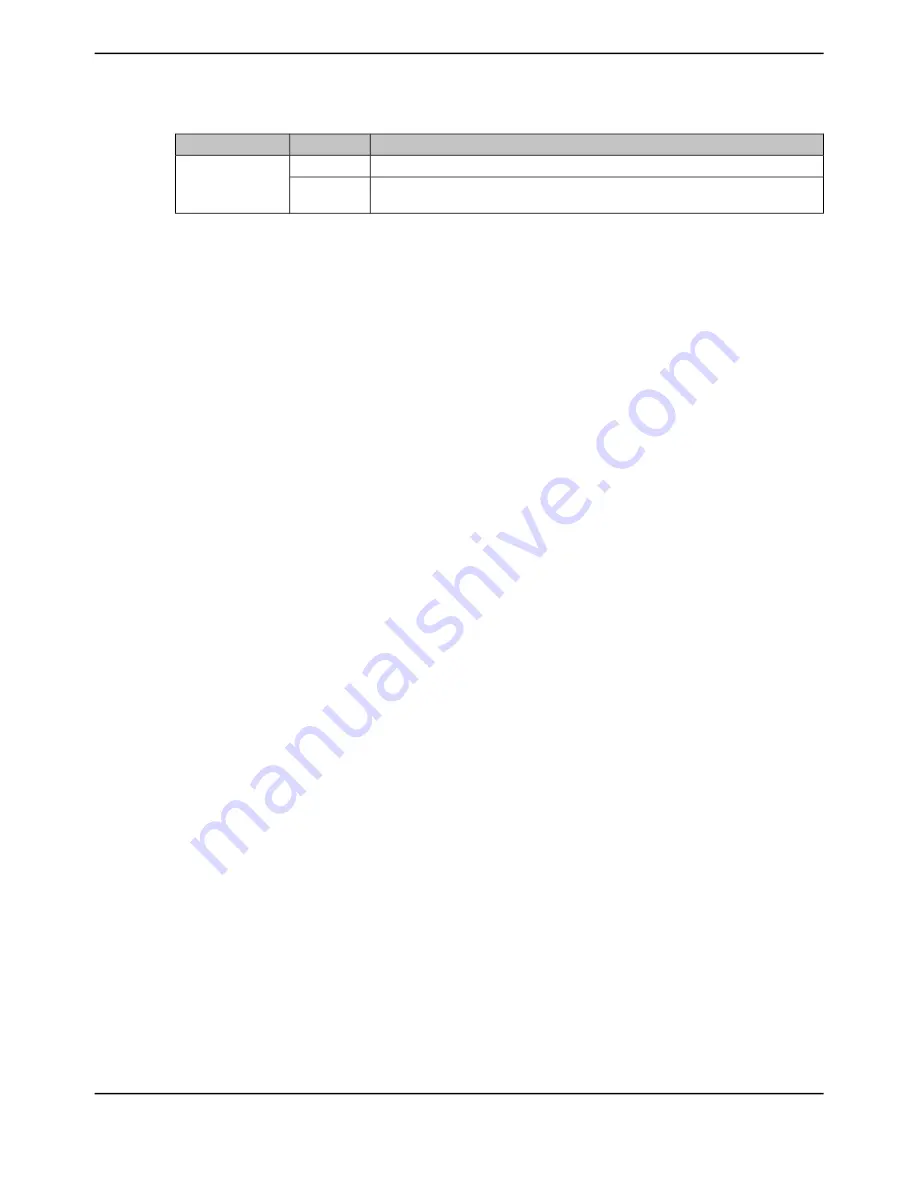
Table 17-3. SSInFss Functionality (continued)
Description
FSSHLDFRM
Mode
SSInFss
is asserted low after every byte of data
0
Advanced/Bi-/Quad-
SSI Mode
New data written to the TX FIFO notifies
SSInFss
to assert low until the Tx FIFO is
empty.
1
17.3.5
High Speed Clock Operation
In master mode, QSSI module can enable a high speed clock by setting the
HSCLKEN
bit in the
SSI
Control 1 (SSICR1)
register. In this mode of operation,
SSInCLK
from the QSSI master operation
is reflected back as a loopback clock, HSPEEDCLK, to the QSSI module. This allows faster timing
since the logic can can be used to adjust clock to external data relationships. HSPEEDCLK captures
RX data in a separate register . This allows the time between the clock as seen by a remote device
and the internal clock to match more closely.
Receive data is captured in a separate register sampled on loop-back clock (HSPEEDCLK) and the
RX FIFO write control registered on HSPEEDCLK. If the
HSCKEN
= 1, the corresponding shift register
and FIFO write enable will be selected for use. This supports faster QSSI master speed.
Note:
For proper functionality of high speed mode, the
HSCLKEN
bit in the
SSICR1
register should
be set before any SSI data transfer or after applying a reset to the QSSI module. In addition,
the
SSE
bit must be set to 0x1 before the
HSCLKEN
bit is set.
17.3.6
Interrupts
The QSSI can generate interrupts when the following conditions are observed:
■ Transmit FIFO service (when the transmit FIFO is half full or less)
■ Receive FIFO service (when the receive FIFO is half full or more)
■ Receive FIFO time-out
■ Receive FIFO overrun
■ End of transmission
■ Receive DMA transfer complete
■ Transmit DMA transfer complete
All of the interrupt events are ORed together before being sent to the interrupt controller, so the
QSSI generates a single interrupt request to the controller regardless of the number of active
interrupts. Each of the seven individual maskable interrupts can be masked by clearing the appropriate
bit in the
SSI Interrupt Mask (SSIIM)
register (see page 1253). Setting the appropriate mask bit
enables the interrupt.
The individual outputs, along with a combined interrupt output, allow use of either a global interrupt
service routine or modular device drivers to handle interrupts. The transmit and receive dynamic
dataflow interrupts have been separated from the status interrupts so that data can be read or written
in response to the FIFO trigger levels. The status of the individual interrupt sources can be read
from the
SSI Raw Interrupt Status (SSIRIS)
and
SSI Masked Interrupt Status (SSIMIS)
registers
(see page 1255 and page 1257, respectively).
The RX FIFO has an associated time-out counter which starts to down count at the same time the
RX FIFO is flagged as not empty by the
RNE
bit in the
SSISR
register. The counter is reset any time
June 18, 2014
1232
Texas Instruments-Production Data
Quad Synchronous Serial Interface (QSSI)
















































