Appendix 1 Explanation of Parameters
MITSUBISHI CNC
364
【
#29079(PR)
】
Master Func. IO Addr. Area PLC side Device
Master function I/O address area read device
Set the device to store the following data:
The data which stores the head address and size (in word form) of the master function receive and
transmit data used by each slave node.
00(HEX): Input data head address of the 1st slave node
01(HEX): Input data size (word count) of the 1st slave node
02(HEX): Output data head address of the 1st slave node
03(HEX): Output data size (word count) of the 1st slave node
04(HEX): Input data head address of the 2nd slave node
:
:
FB(HEX): Output data size (word count) of the 63rd slave node
---Setting range---
Within the number of device points set in the PC parameter's device setting.
【
#29080(PR)
】
Master Func. Receive Data Module side Transfer Cont.
Master function receive data read word count
Set a read word count of the data received from each slave node.
The standard setting is "256".
---Setting range---
1 to 256
【
#29081(PR)
】
Master Func. Receive Data PLC side Device
Master function receive data read device
Set the device to read the data received from each slave node.
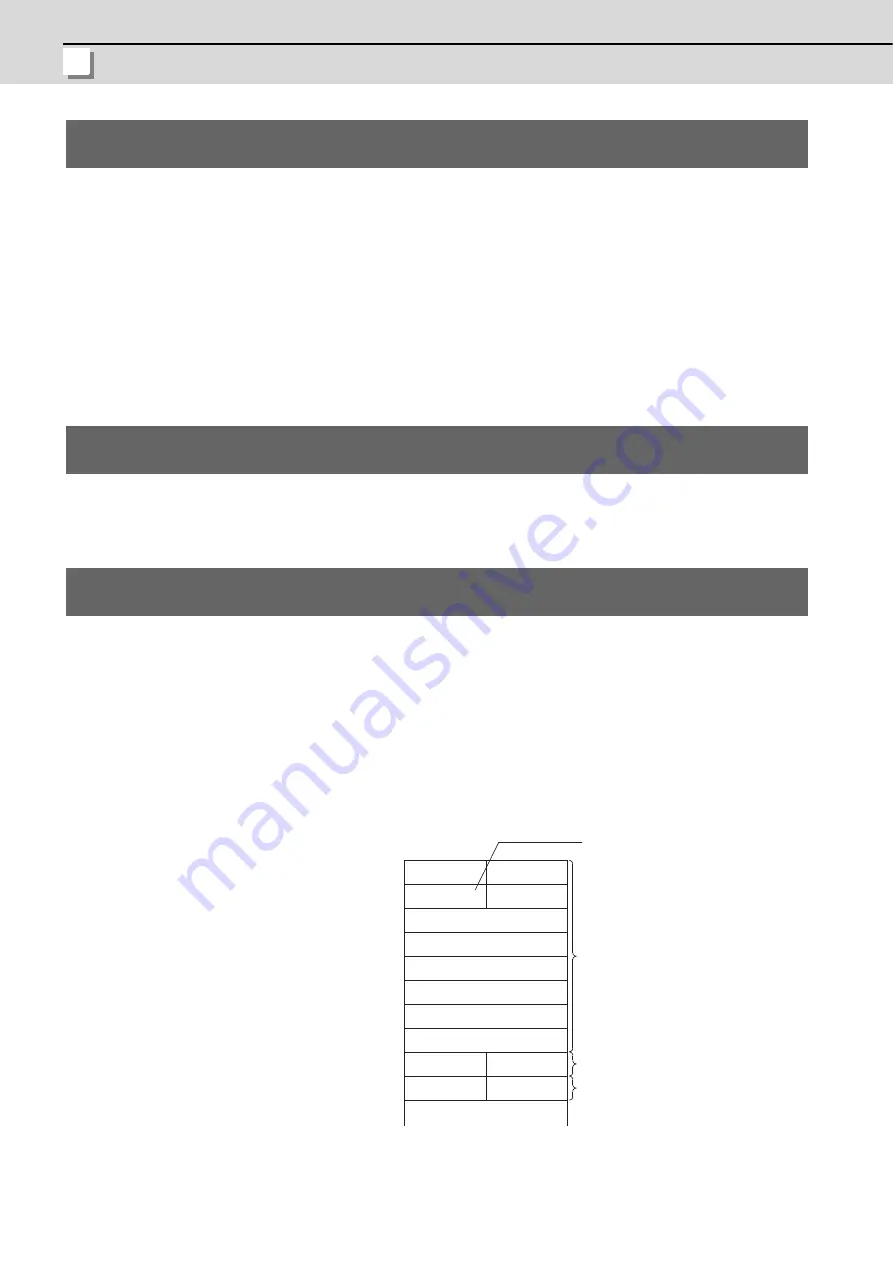
<Data configuration>
The data is aligned at the word boundaries of the slave nodes before stored.
Double-word data is stored in the order of lower word first and higher word next.
If there is an odd number of byte input modules, one byte of empty area will be inserted for alignment
at the word boundary. Bit input modules are treated in the same way as the byte input modules.
---Setting range---
Within the number of device points set in the PC parameter's device setting.
<Example>
Number of byte input modules = 3
1st node -
2nd node -
3rd node -
Number of word input modules = 2
Number of double-word input modules = 2
Number of byte input modules = 1
Number of byte input modules = 1
Receive data buffer
Offset from head address
0000
H
0001
H
0002
H
0003
H
0004
H
0005
H
0006
H
0007
H
0008
H
0009
H
Input data of the 1st node
Input data of the 2nd node
Input data of the 3rd node
2nd byte module
1st byte module
3rd byte module
Empty
1st word module
2nd word module
Lower word of the
1st double-word module
Higher word of the
1st double-word module
Lower word of the
2nd double-word module
Higher word of the
2nd double-word module
1st byte module
1st byte module
Empty
Empty
Slave node configuration
If there is an odd number
of byte input modules,
one byte of empty area
will be inserted.
Summary of Contents for C70
Page 1: ......
Page 3: ......
Page 9: ......
Page 11: ......
Page 13: ......
Page 18: ...1 1 Outline ...
Page 21: ...1 Outline MITSUBISHI CNC 4 ...
Page 22: ...5 2 GOT Initial Setup ...
Page 73: ...2 GOT Initial Setup MITSUBISHI CNC 56 ...
Page 74: ...57 3 PLC CPU Initial Setup ...
Page 91: ...3 PLC CPU Initial Setup MITSUBISHI CNC 74 ...
Page 92: ...75 4 CNC CPU Initial Setup ...
Page 105: ...4 CNC CPU Initial Setup MITSUBISHI CNC 88 ...
Page 106: ...89 5 Connecting and Setting up Multiple CNC CPU Modules ...
Page 115: ...5 Connecting and Setting up Multiple CNC CPU Modules MITSUBISHI CNC 98 ...
Page 116: ...99 6 Setting Machine Parameters ...
Page 130: ...113 7 Setting the Position Detection System ...
Page 153: ...7 Setting the Position Detection System MITSUBISHI CNC 136 ...
Page 154: ...137 8 Deceleration Check ...
Page 159: ...8 Deceleration Check MITSUBISHI CNC 142 ...
Page 160: ...143 9 Setting the Tool Entry Prohibited Range ...
Page 169: ...9 Setting the Tool Entry Prohibited Range MITSUBISHI CNC 152 ...
Page 170: ...153 10 Data Backup and Restoration ...
Page 184: ...167 Appendix 1 Explanation of Parameters ...
Page 435: ...Appendix 1 Explanation of Parameters MITSUBISHI CNC 418 ...
Page 436: ...419 Appendix 2 Explanation of Alarms ...
Page 608: ...591 Appendix 3 Display on 7 segment LED ...
Page 624: ......
Page 628: ......
















































