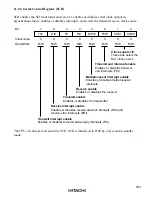
345
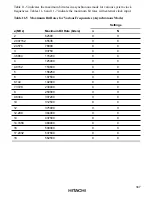
Table 11-4 Examples of Bit Rates and BRR Settings in Synchronous Mode
ø (MHz)
Bit Rate
2
4
8
10
16
18
(bits/s)
n
N
n
N
n
N
n
N
n
N
n
N
110
3
70
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
250
2
124
2
249
3
124
—
—
3
249
—
—
500
1
249
2
124
2
249
—
—
3
124
3
140
1 k
1
124
1
249
2
124
—
—
2
249
3
69
2.5 k
0
199
1
99
1
199
1
249
2
99
2
112
5 k
0
99
0
199
1
99
1
124
1
199
1
224
10 k
0
49
0
99
0
199
0
249
1
99
1
112
25 k
0
19
0
39
0
79
0
99
0
159
0
179
50 k
0
9
0
19
0
39
0
49
0
79
0
89
100 k
0
4
0
9
0
19
0
24
0
39
0
44
250 k
0
1
0
3
0
7
0
9
0
15
0
17
500 k
0
0
*
0
1
0
3
0
4
0
7
0
8
1 M
0
0
*
0
1
—
—
0
3
0
4
2 M
0
0
*
—
—
0
1
—
—
2.5 M
—
—
0
0
*
—
—
—
—
4 M
0
0
*
—
—
Note:
Settings with an error of 1% or less are recommended.
Legend
Blank: No setting available
—:
Setting possible, but error occurs
*
:
Continuous transmission/reception not possible
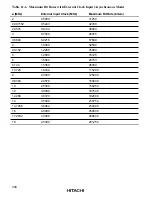
The BRR setting is calculated as follows:
Asynchronous mode:
N =
ø
64
×
2
2n-1
×
B
×
10
6
– 1
Synchronous mode:
N =
ø
8
×
2
2n-1
×
B
×
10
6
– 1
B:
Bit rate (bits/s)
N:
BRR setting for baud rate generator (0
≤
N
≤
255)
ø:
System clock frequency (MHz)
n:
Baud rate generator clock source (n = 0, 1, 2, 3)
(For the clock sources and values of n, see the following table.)