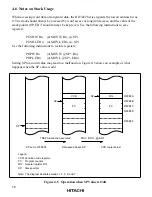
90
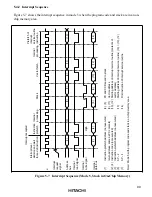
5.3 Interrupt Sources
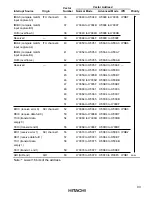
The interrupt sources include external interrupts (NMI, IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
and IRQ
0
) and 25
internal interrupts.
5.3.1 External Interrupts
There are five external interrupts: NMI, and IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, and IRQ
0
. Of these, NMI, IRQ
0
,
IRQ
1
, can be used to exit software standby mode.
NMI: NMI is the highest-priority interrupt and is always accepted, regardless of the states of the
I and UI bits in CCR. The NMIEG bit in SYSCR selects whether an interrupt is requested by the
rising or falling edge of the input at the NMI pin. NMI interrupt exception handling has vector
number 7.
IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, IRQ
0
Interrupts: These interrupts are requested by input signals at pins
IRQ
5
,
IRQ
4
,
IRQ
1
,
IRQ
0
. The IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, IRQ
0
interrupts have the following features.
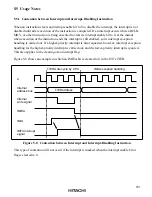
•
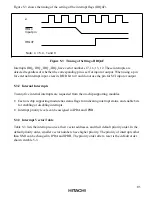
ISCR settings can select whether an interrupt is requested by the low level of the input at pins
IRQ
5
,
IRQ
4
,
IRQ
1
,
IRQ
0
, or by the falling edge.
•
IER settings can enable or disable the IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, IRQ
0
interrupts.
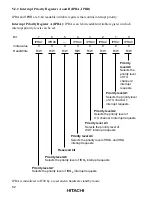
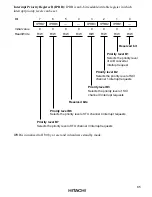
Interrupt priority levels can be assigned by three bits in IPRA (IPRA7, IPRA6, and IPRA4).
•
The status of IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, IRQ
0
interrupt requests is indicated in ISR. The ISR flags can
be cleared to 0 by software.
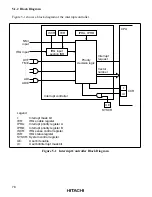
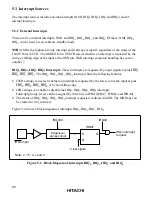
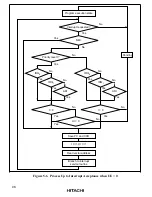
Figure 5-2 shows a block diagram of interrupts IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, IRQ
0
.
input
Edge/level
sense circuit
IRQnSC
IRQnF
S
R
Q
IRQnE
IRQn interrupt
request
Clear signal
IRQn
Note: n = 5, 4, 1 and 0
Figure 5-2 Block Diagram of Interrupts IRQ
5
, IRQ
4
, IRQ
1
, and IRQ
0