2
3
16. Ensure the dilator is securely connected with the sheath prior to advancing otherwise only the
sheath may advance into the vessel and the sheath tip may cause damage to the vessel.
17. Ensure the dilator is in place within the sheath before advancing the sheath as otherwise
damage may be caused to the vessel.
18. Do not place sutures on the sheath tubing since this may restrict access/flow through the
sheath. When puncturing, suturing or incising near the sheath be careful not to damage the
sheath. Proper functioning of the sheath depends on its integrity. Care should be used when
handling the sheath.
19. If using fluid injection through the 3 way stopcock, ensure the dilator or procedural device is
not in place at the same time.
20. If resistance is felt during post-procedure withdrawal of the procedural device, it is
recommended to remove the procedural device, guidewire, and sheath as a single unit.
21. In order to activate the hydrophilic coating, it is recommended to wet the
Halo One™
Thin-Walled Guiding Sheath with heparinized saline solution immediately prior to its insertion
in the body. Failure to activate the coating may lead to sub-optimal trackability of the sheath.
To maintain lubricity this surface must be kept completely wet.
22. Proper functioning of the
Halo One™
Thin-Walled Sheath depends on its integrity. Care
should be used when handling the sheath. Damage may result from kinking, stretching, or
forceful wiping of the
Halo One™
Thin-Walled Guiding Sheath. Do not continue to use the
sheath if the shaft has been bent or kinked.
POTENTIAL ADVERSE EFFECTS
Potential adverse effects that may result from a percutaneous vascular procedure (directly or
indirectly associated with the device) may include, but are not limited to:
•
Air embolism
•
Aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm
•
Arteriovenous fistula
•
Compartment Syndrome
• Death
• Embolism
• Endocarditis
• Hematoma
•
Hemorrhage, including bleeding at the puncture site
•
Intimal tear
•
Radial artery occlusion/spasm
• Sepsis/infection/inflammation
•
Tissue necrosis
•
Thrombus formation
•
Vessel spasm, perforation or dissection
•
Potential systemic indirect/inherent adverse effects related to general endovascular
procedures may include, but are not limited to:
• Arrhythmias
•
Drug reactions, allergic reaction to contrast media
• Hypotension/hypertension
•
Pain and tenderness
STORAGE
Store in a cool, dry, dark place. Rotate inventory so that the catheter and other dated products are
used prior to the “Use By” date. Do not use if packaging is damaged or opened.
DIRECTIONS FOR USE
Equipment Required
•
Sterile saline solution (heparinized)
•
Sterile saline solution (heparinized) / Contrast medium (2:1 ratio recommended)
•
Luer lock syringe/inflation device with manometer (10 ml or larger)
•
0.035" (0.89 mm) guidewire or 0.018" (0.46 mm) guidewire as labeled per device
Halo One™
Thin-Walled Guiding Sheath Preparation
1. Verify the French size is suitable for the procedure and can accommodate the required
procedural devices as labeled (Figure 3). Remove sheath and dilator from package.
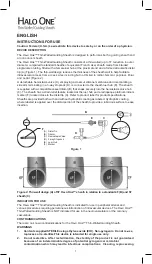
2. Prior to use, the air in the sheath and dilator should be removed. To facilitate purging, the
device is packaged with the dilator inside the sheath in a reverse direction allowing both to
be flushed simultaneously. Select a syringe or inflation device with a 10 ml or larger capacity
and fill approximately half of it with sterile saline solution. Prepare the lumen by connecting
the syringe or inflation device containing the solution into the stopcock on the side-port of the