2-87
CAPACITY CONTROL MECHANISM
CAPACITY CONTROL MECHANISM
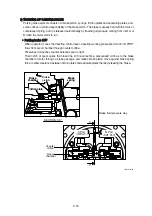
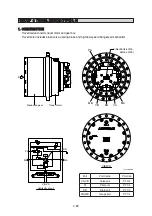
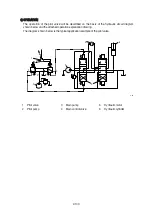
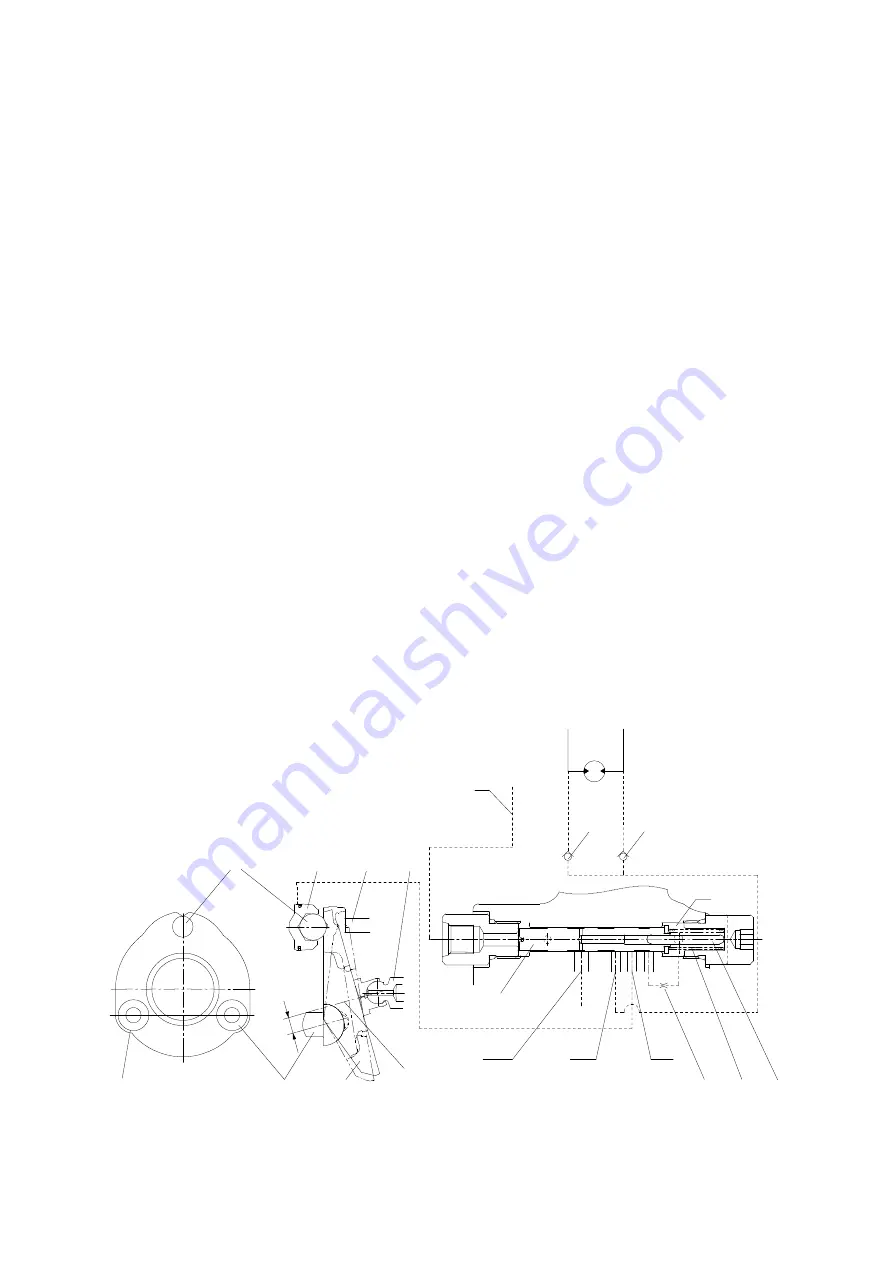
Figure typically shows the capacity control mechanism.
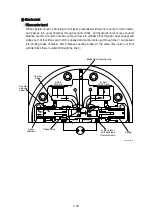
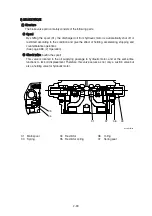
When high speed pilot line is charged with the pressure P
A
that overcome the spring (44), the
spring (44) is compressed and spool (40) shifts to the right to connect the port P and port C.
Then, the highest pressure is selected by the check valve (50) from inlet and outlet pressure of the
motor and high speed pilot line pressure and pushes shifter piston (4). As a result, swash plate (11)
turns around the line L which connect the two steel balls (10) as shown by dotted lines. The turn
stops at the stopper (1-1) of casing and swash plate (11) keeps the position.
In this case, the piston stroke become shorter and motor capacity become smaller and motor
rotates faster, around 1.60 times, by the same volume of oil.
When no pressure is in the high speed pilot line P
A
, spool (40) is pushed back by the spring (44)
and pressure that pressed the shifter piston (4) is released to the hydraulic tank through restrictor
(55).
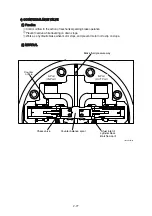
Here, nine pistons are there and they equally spaced on the swash plate (11). The force that
summed up those of pistons comes to almost the center of the swash plate (11) as shown. Since
the steel balls (10) are off-set by S from the center, the rotating force of product S and the force
moves swash plate (11) to the former position and the speed returns to low.
When the power demand exceeds the engine power, such as in steep slope climbing or turning at
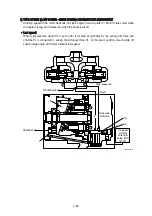
high speed mode, the system step down to the low speed automatically. The mechanism is that:
pump pressure is led to the port P
B
and this pressure activate on pin (43). When the pressure at P
B
exceeds predetermined value, spool (40) returns to the left by the counter-pressure against pin (43)
and the pressure on the shifter piston (4) through port C is released to the tank and the motor
comes to low speed.
When P
B
goes down, the spool (40) moves to the right and the speed become high.
3)
3)
High speed pilot line
(External Pilot)
To counterbalance valve
(Brake valve)
MB
MA
50
50
9
4
1-1
16
10
10
Load
application point
L
L
S
40
P
C
VA or VB
55
44
43
T
P
A
P
B
11
125LCR2TM19
Содержание HX145 LCR
Страница 11: ...SECTION 1 GENERAL SECTION 1 GENERAL Group 1 Safety Hints 1 1 Group 2 Specifications 1 10...
Страница 204: ...4 5 MEMORANDUM HYUNDAI HEAVY INDUSTRIES CO LTD CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT DIV...
Страница 553: ...8 82 Insert O rings to the relief valve 30 and reassemble them to rear cover 20 This completes assembly 17 32038SM42...
Страница 627: ...8 155 125LCR8TM30 Turn casing 1 upside down and remove oil seal 3 using jig 29...
Страница 636: ...8 164 125LCR8TM61 After assembling spring 44 in order clamp plug 41 Tightening torque 5 kgf m 36 lbf ft 31...
Страница 657: ...8 185 8 185 Remove lock nut 22 and then boot 23 14 36078RL14 2507ARL10...
Страница 668: ...8 196 14 15 3 Install cover 3 to body 1 and tighten bolts 14 Torque 10 12 5 kgf m 72 3 90 4 lbf ft 7 21078DA10...