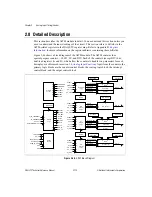
Chapter 2
Analog Input Timing/Control
©
National Instruments Corporation
2-115
DAQ-STC Technical Reference Manual
FSC_SRC
Fast Edge of SC Source—This signal synchronizes signals that arrive
asynchronously but need to be retimed by SC_SRC. In the internal
CONVERT mode, FSC_SRC is equal to the inactive (falling) edge of
SI2_SRC. In the external CONVERT mode, FSC_SRC is equal to
FSCLK.
IN_TIMEBASE2
Slow Internal Timebase—This signal is derived from the
IN_TIMEBASE signal and is usually configured to be 100 kHz. Related
bitfields: Slow_Internal_Time_Divide_By_2, Slow_Internal_Timebase.
SC_CE
SC Count Enable—This signal enables and disables the SC counter.
Refer to section
, for the SC_CE logic equations.
SC_CLK
SC Clock—This is the actual clock signal for the SC counter and the SC
counter control logic. When the counter is not armed, SC_CLK is
derived from the write strobe for AI_Command_1_Register, so that the
counter can be loaded using the load command. When the counter is
armed, SC_CLK is the same as SC_SRC. Related bitfields:
AI_SC_Load.
SC_GATE
SC Counter Gate—This signal is generated by the SC control logic.
SC_GATE conditions the external CONVERT so that CONVERT
passes through only when the SC counter is enabled to count. It is set by
the assertion of START1 when SC_ARM is true and is cleared when the
SC counter returns to the WAIT1 state. Related bitfields:
AI_SC_Gate_Enable, AI_SC_Gate_St.
SC_HOLD
SC Hold—This signal controls the SC save register. If SC_HOLD = 0,
then the SC save register tracks the SC counter output. If SC_HOLD =
1, then the SC save register latches the SC counter output on the next
SC_CLK.
SCKG
Sample Clock Gate—In the internal CONVERT mode, SCKG is
SI2_TC. In the external CONVERT mode, SCKG is 1.
SCLK
Sample Clock—In the internal CONVERT mode, SCLK is the signal
SI2_TC. In the external CONVERT mode, SCLK is the signal FSCLK
after it passes through a delay gate. The delay gate is provided so that
signals synchronized to FSCLK have sufficient time to settle to a known
state before being used by SCLK.
Table 2-9.
Internal Signals (Continued)
Signal
Description