11-4
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 11 Configuring Radio Resource ManagementWireless Device Access
Overview of Radio Resource Management
•
Utilization
—When utilization monitoring is enabled, capacity calculations can consider that some
access points are deployed in ways that carry more traffic than other access points (for example, a
lobby versus an engineering area). The controller can then assign channels to improve the access
point with the worst performance (and therefore utilization) reported.
•
Load
—Load is taken into account when changing the channel structure to minimize the impact on
clients currently in the wireless LAN. This metric keeps track of every access point’s transmitted
and received packet counts to determine how busy the access points are. New clients avoid an
overloaded access point and associate to a new access point. This parameter is disabled by default.
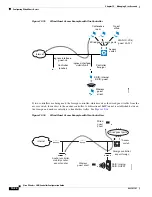
The controller combines this RF characteristic information with RRM algorithms to make system-wide
decisions. Conflicting demands are resolved using soft-decision metrics that guarantee the best choice
for minimizing network interference. The end result is optimal channel configuration in a
three-dimensional space, where access points on the floor above and below play a major factor in an
overall wireless LAN configuration.
In controller software releases prior to 5.1, only radios using 20-MHz channels are supported by DCA.
In controller software release 5.1 or later, DCA is extended to support 802.11n 40-MHz channels in the
5-GHz band. 40-MHz channelization allows radios to achieve higher instantaneous data rates
(potentially 2.25 times higher than 20-MHz channels). In controller software release 5.1 or later, you can
choose between DCA working at 20 or 40 MHz.
Note
Radios using 40-MHz channels in the 2.4-GHz band are not supported by DCA.
Coverage Hole Detection and Correction
The RRM coverage hole detection algorithm is designed to detect areas of radio coverage in a wireless
LAN that are below the level needed for robust radio performance. This feature can alert you to the need
for an additional (or relocated) lightweight access point.
If clients on a lightweight access point are detected at threshold levels (RSSI, failed client count,
percentage of failed packets, and number of failed packets) lower than those specified in the RRM
configuration, the access point sends a “coverage hole” alert to the controller. The alert indicates the
existence of an area where clients are continually experiencing poor signal coverage, without having a
viable access point to which to roam. The controller discriminates between coverage holes that can and
cannot be corrected. For coverage holes that can be corrected, the controller mitigates the coverage hole
by increasing the transmit power level for that specific access point. The controller does not mitigate
coverage holes caused by clients that are unable to increase their transmit power or are statically set to
a power level because increasing their downstream transmit power is not a remedy for poor upstream
performance and might increase interference in the network.
Note
While transmit power control and DCA can operate in multi-controller environments (based on RF
domains), coverage hole detection is performed on a per-controller basis. In controller software release
5.2, you can disable coverage hole detection on a per-WLAN basis. See the
Detection per WLAN” section on page 6-54
for more information.