6-19
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 6 Configuring WLANsWireless Device Access
Configuring WLANs
Guidelines for Using Peer-to-Peer Blocking
Follow these guidelines when using peer-to-peer blocking:
•
In controller software releases prior to 4.2, the controller forwards Address Resolution Protocol
(ARP) requests upstream (just like all other traffic). In controller software release 4.2 or later, ARP
requests are directed according to the behavior set for peer-to-peer blocking.
•
Peer-to-peer blocking does not apply to multicast traffic.
•
Locally switched hybrid-REAP WLANs and hybrid-REAP access points in standalone mode do not
support peer-to-peer blocking.
•
If you upgrade to controller software release 4.2 or later from a previous release that supports global
peer-to-peer blocking, each WLAN is configured with the peer-to-peer blocking action of
forwarding traffic to the upstream VLAN.
Using the GUI to Configure Peer-to-Peer Blocking
Follow these steps to configure a WLAN for peer-to-peer blocking using the GUI.
Step 1
Click
WLANs
to open the WLANs page.
Step 2
Click the ID number of the WLAN for which you want to configure peer-to-peer blocking.
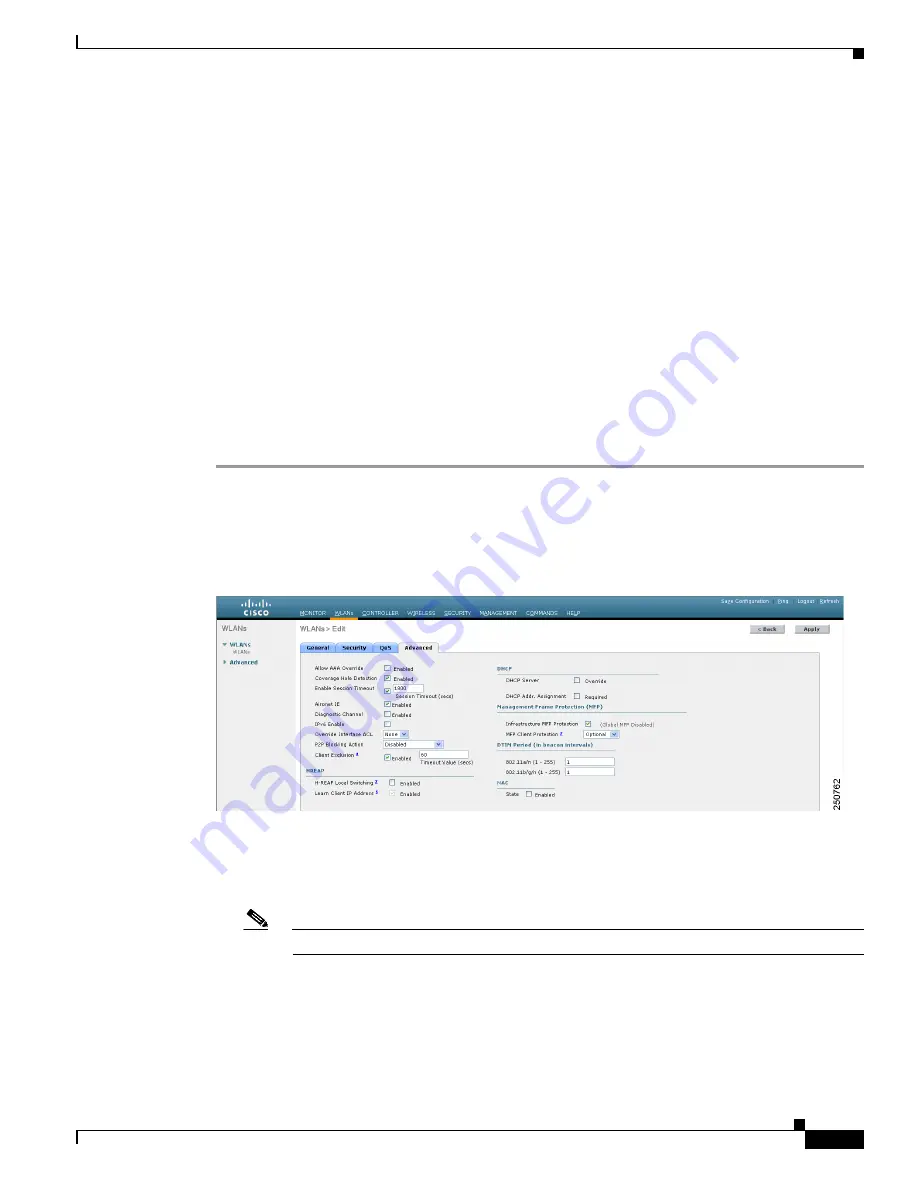
Step 3
Click the
Advanced
tab to open the WLANs > Edit (Advanced) page (see
).
Figure 6-10
WLANs > Edit (Advanced) Page
Step 4
Choose one of the following options from the P2P Blocking drop-down box:
•
Disabled
—Disables peer-to-peer blocking and bridges traffic locally within the controller whenever
possible. This is the default value.
Note
Traffic is never bridged across VLANs in the controller.
•
Drop
—Causes the controller to discard the packets.
•
Forward-UpStream
—Causes the packets to be forwarded on the upstream VLAN. The device
above the controller decides what action to take regarding the packets.






























