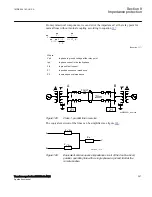
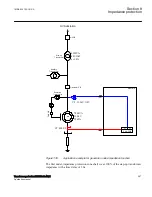
Where:
Z
AT
and Z
CT
is the line impedance from the A respective C station to the T point.
I
A
and I
C
is fault current from A respective C station for fault between T and B.
V2/V1
Transformation ratio for transformation of impedance at V1 side of the transformer to
the measuring side V2 (it is assumed that current and voltage distance function is
taken from V2 side of the transformer).
Z
TF
is the line impedance from the T point to the fault (F).
Z
Trf
Transformer impedance
For this example with a fault between T and B, the measured impedance from the T
point to the fault will be increased by a factor defined as the sum of the currents from T
point to the fault divided by the IED current. For the IED at C, the impedance on the
high voltage side V1 has to be transferred to the measuring voltage level by the
transformer ratio.
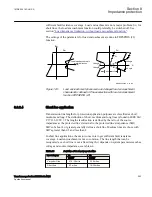
Another complication that might occur depending on the topology is that the current
from one end can have a reverse direction for fault on the protected line. For example,
for faults at T the current from B might go in reverse direction from B to C depending
on the system parameters (see the dotted line in figure
protection in B to T will measure wrong direction.
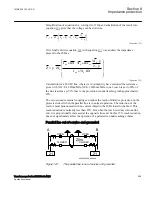
In three-end application, depending on the source impedance behind the IEDs, the
impedances of the protected object and the fault location, it might be necessary to
accept zone 2 trip in one end or sequential trip in one end.
Generally for this type of application it is difficult to select settings of zone 1 that both
gives overlapping of the zones with enough sensitivity without interference with other
zone 1 settings, that is, without selectivity conflicts. Careful fault calculations are
necessary to determine suitable settings and selection of proper scheme
communication.
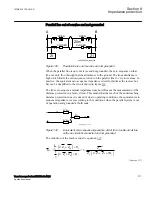
Fault resistance
M17048-597 v8
The performance of distance protection for single phase-to-ground faults is very
important, because normally more than 70% of the faults on transmission lines are
single phase-to-ground faults. At these faults, the fault resistance is composed of three
parts: arc resistance, resistance of a tower construction, and tower-footing resistance.
The arc resistance can be calculated according to Warrington's formula:
Section 8
1MRK 504 163-UUS A
Impedance protection
274
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI
Application manual
Содержание RELION RET670
Страница 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Transformer protection RET670 Version 2 2 ANSI Application manual ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 48: ...42 ...
Страница 64: ...58 ...
Страница 74: ...68 ...
Страница 104: ...98 ...
Страница 194: ...188 ...
Страница 518: ...512 ...
Страница 618: ...612 ...
Страница 648: ...642 ...
Страница 666: ...660 ...
Страница 672: ...666 ...
Страница 682: ...676 ...
Страница 844: ...838 ...
Страница 868: ...862 ...
Страница 956: ...950 ...
Страница 964: ...958 ...
Страница 1004: ...998 ...
Страница 1014: ...1008 ...
Страница 1015: ...1009 ...