current until it develops into an ground or phase fault. For this reason it is important
that the differential protection has a high level of sensitivity and that it is possible to
use a sensitive setting without causing unwanted operations during external faults.
It is important that the faulty transformer be disconnected as fast as possible. As the
differential protection is a unit protection it can be designed for fast tripping, thus
providing selective disconnection of the faulty transformer. The differential protection
should never operate on faults outside the protective zone.
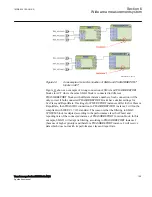
A transformer differential protection compares the current flowing into the transformer
with the current leaving the transformer. A correct analysis of fault conditions by the
differential protection must take into consideration changes due to the voltage, current
and phase angle caused by the protected transformer. Traditional transformer
differential protection functions required auxiliary transformers for correction of the
phase shift and ratio. The numerical microprocessor based differential algorithm as
implemented in the IED compensates for both the turn-ratio and the phase shift
internally in the software. No auxiliary current transformers are necessary.
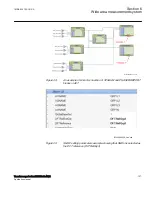
The differential current should theoretically be zero during normal load or external
faults if the turn-ratio and the phase shift are correctly compensated. However, there
are several different phenomena other than internal faults that will cause unwanted and
false differential currents. The main reasons for unwanted differential currents may be:
•
mismatch due to varying tap changer positions
•
different characteristics, loads and operating conditions of the current transformers
•
zero sequence currents that only flow on one side of the power transformer
•
normal magnetizing currents
•
magnetizing inrush currents
•
overexcitation magnetizing currents
7.1.3
Setting guidelines
IP14936-1 v2
M15266-4 v5
The parameters for the Transformer differential protection function are set via the local
HMI or Protection and Control IED Manager (PCM600).
7.1.3.1
Restrained and unrestrained differential protection
M15266-289 v10
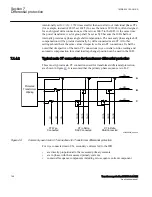
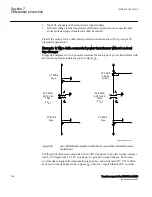
To make a differential IED as sensitive and stable as possible, restrained differential
protections have been developed and are now adopted as the general practice in the
protection of power transformers. The protection should be provided with a
proportional bias, which makes the protection operate for a certain percentage
differential current related to the current through the transformer. This stabilizes the
protection under through fault conditions while still permitting the system to have good
basic sensitivity. The bias current can be defined in many different ways. One classical
Section 7
1MRK 504 163-UUS A
Differential protection
136
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI
Application manual
Содержание RELION RET670
Страница 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Transformer protection RET670 Version 2 2 ANSI Application manual ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 48: ...42 ...
Страница 64: ...58 ...
Страница 74: ...68 ...
Страница 104: ...98 ...
Страница 194: ...188 ...
Страница 518: ...512 ...
Страница 618: ...612 ...
Страница 648: ...642 ...
Страница 666: ...660 ...
Страница 672: ...666 ...
Страница 682: ...676 ...
Страница 844: ...838 ...
Страница 868: ...862 ...
Страница 956: ...950 ...
Страница 964: ...958 ...
Страница 1004: ...998 ...
Страница 1014: ...1008 ...
Страница 1015: ...1009 ...