SIPART DR20
Project Planning Manual
Since the control result thus obtained does not completely meet the requirements in most cases,
the switching frequency is increased and the amplitude of the oscillation is thus reduced. The
performance of a P or PI controller can thus be achieved in many cases using a two-position
controller. In the SIPART DR20 the control amplifier is followed by a duty factor converter with
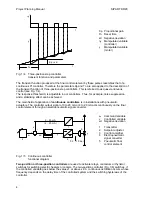
adjustable period, resulting in a PID two- position controller (Fig. 1/7).
w
2
1
x
y
z
+
-
1. Controller
2. Controlled
system
x
x1
x2
OFF
ON
y
ON
OFF
t
t
Fig. 1/6 Two-position controller without feedback
w
2
1
x
-
+
xd
3
4
5
1. Setpoint adjuster
2. Control amplifier
3. Duty factor converter
4. Controlled system
5. Transmitter
Fig. 1/7 SIPART DR20 two-position controller
In the case of controllers with mechanical contacts, the switching frequency possibly is limited
because of the contact life. However, if thyristor units are used as switching elements, the
switching frequency can be increased.
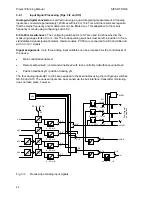
The control problem often requires the controller action to be divided between various final control
elements or manipulated variables, e.g. for heating and cooling. Two- position controllers are used
for these problems where the manipulated variables are divided into two sections and assigned to
two outputs. An adjustable dead zone is present between the two sections. A duty factor of 0 to
100 % is possibly in each section.
These controllers are also referred to as three-position controllers.
9