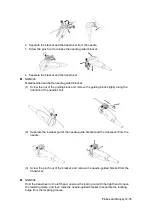
Acoustic Output 14-5
Although the attenuation coefficient chosen, 0.3 dB/cm/MHz, is significantly lower than any
specific solid tissue in the body, this value was chosen to account for fetal examinations. In
early trimester ultrasound fetal examinations, there may be a significant fluid path between
the transducer and the fetus, and the attenuation of fluid is very small. Therefore the
attenuation coefficient was lowered to account for this case.
14.7.2 Limits of Acoustic Output
In accordance with the FDA Track 3 requirements, the derating (or attenuated) approach
was incorporated into the FDA Acoustic Output Limits, as listed below. The maximum
acoustic output level from any transducer in any operating mode is expected to fall below
these limits.
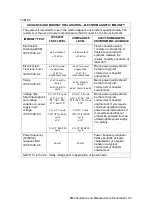
FDA Maximum Acoustic Output Limits for Track 3 (Attenuated Values)
Application
I
spta.3
(mW/cm
2
)
I
sppa.3
(W/cm
2
)
Or
MI
Regions
(except eyes)
720
≤ 190
≤ 1.9
14.7.3 Differences between Actual and Displayed MI
and TI
In operation, the system will display to the operator the Acoustic Output Parameters Thermal
Index, TI, or Mechanical Index, MI (or sometimes both parameters simultaneously). These
parameters were developed as general indicators of risk from either thermal or mechanical
action of the ultrasound wave. They serve to indicate to the operator whether a particular
setting of the system increases or decreases the possibility of Thermal or Mechanical effect.
More specifically, they were designed to assist in the implementation of the ALARA principle.
As an operator changes a given system control, the potential effect of the change in output
will be indicated. However, the Thermal Index is not the same as temperature rise in the
body, for several reasons. First of all, in order to provide a single display index to you, a
number of simplifying assumptions had to be made. The biggest assumption was the use of
the attenuating formula described above, which is much lower than the actual value for most
tissues within the body. Scanning through muscle or organ tissue, for example, will produce
much higher attenuation than 0.3 dB/cm/MHz. There were also significant simplifications
made for the thermal properties of tissue. Therefore, scanning through highly perfused tissue,
such as the heart or vasculature, will produce significantly less thermal effect than that
suggested by the Thermal Index.
Similarly, the Mechanical Index was derived to indicate the relative possibility of mechanical
(cavitation) effects. The MI is based on the derated peak-rarefactional pressure and the
center frequency of the ultrasound wave. The actual peak-rarefactional pressure is affected
by the actual attenuation caused by tissue in the path between the transducer and the focal
point. Again, all solid tissues within the body have higher attenuation than the proscribed 0.3
dB/cm/MHz value, and therefore, the actual peak-rarefactional pressure will be lower.
Further, the actual peak-rarefactional pressure will change depending upon the region of the
body being scanned.
For these reasons, the TI and MI displays should only be used to assist the operator in
implementing ALARA at the time of the animal examination.
Summary of Contents for DP-50 Exp Vet
Page 2: ......
Page 34: ...2 6 System Overview 2 6 Introduction of Each Unit Right View Left View...
Page 42: ......
Page 68: ......
Page 128: ......
Page 148: ......
Page 166: ...10 18 DICOM For details on tast manager see 9 6 Animal Task Manager...
Page 180: ......
Page 220: ......
Page 224: ......
Page 236: ......
Page 242: ......
Page 248: ......
Page 342: ...D 2 Printer Adapter Type Model SONY X898MD...
Page 343: ...P N 046 017713 02 1 0...