PIM Source-Specific Mode |
777
35
PIM Source-Specific Mode
PIM Source-Specific Mode
is supported on platforms:
c e s
PIM-SSM is supported on the E-Series ExaScale platform with FTOS 8.1.1.0 and later.
PIM-Source-Specific Mode (PIM-SSM) is a multicast protocol that forwards multicast traffic from a single
source to a subnet. In the other versions of Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM), a receiver subscribes to
a group only. The receiver receives traffic not just from the source in which it is interested but from all
sources sending to that group. PIM-SSM requires that receivers specify the sources in which they are
interested using IGMPv3 include messages to avoid receiving unwanted traffic.
PIM-SSM is more efficient than PIM-SM because it immediately creates shortest path trees (SPT) to the
source rather than first using shared trees. PIM-SM requires a shared tree rooted at the RP because
IGMPv2 receivers do not know about the source sending multicast data. Multicast traffic passes from the
source to the receiver through the RP, until the receiver learns the source address, at which point it switches
to the SPT. PIM-SSM uses IGMPv3. Since receivers subscribe to a source and group, the RP and shared
tree is unnecessary, so only SPTs are used. On Dell Force10 systems, it is possible to use PIM-SM with
IGMPv3 to achieve the same result, but PIM-SSM eliminates the unnecessary protocol overhead.
PIM-SSM also solves the multicast address allocation problem. Applications should use unique multicast
addresses because if multiple applications use the same address, receivers receive unwanted traffic.
However, global multicast address space is limited. Currently GLOP/EGLOP is used to statically assign
Internet-routable multicast addresses, but each autonomous system number yields only 255 multicast
addresses. For short-term applications, an address could be leased, but no global dynamic multicast
address allocation scheme has been accepted yet. PIM-SSM eliminates the need for unique multicast
addresses because routing decisions for (S1, G1) are independent from (S2, G1). As a result, subnets do not
receive unwanted traffic when multiple applications use the same address.
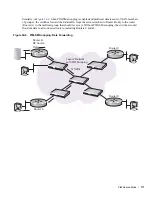
In
Figure 35-1
, Receiver 1 is an IGMPv2 host. The packets for group 239.0.0.2 travel to it first via the RP,
then by the SPT. Receiver 2 is an IGMPv3 host. The packets for group 239.0.0.1 travel only via the STP.
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...