404
|
Internet Group Management Protocol
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
IGMP version 2
IGMP version 2 improves upon version 1 by specifying IGMP Leave messages, which allows hosts to
notify routers that they no longer care about traffic for a particular group. Leave messages reduce the
amount of time that the router takes to stop forwarding traffic for a group to a subnet (leave latency) after
the last host leaves the group. In version 1 hosts quietly leave groups, and the router waits for a query
response timer several times the value of the query interval to expire before it stops forwarding traffic.
To receive multicast traffic from a particular source, a host must join the multicast group to which the
source is sending traffic. A host that is a member of a group is called a
receiver
. A host may join many
groups, and may join or leave any group at any time. A host joins and leaves a multicast group by sending
an IGMP message to its IGMP Querier. The querier is the router that surveys a subnet for multicast
receivers, and processes survey responses to populate the multicast routing table.
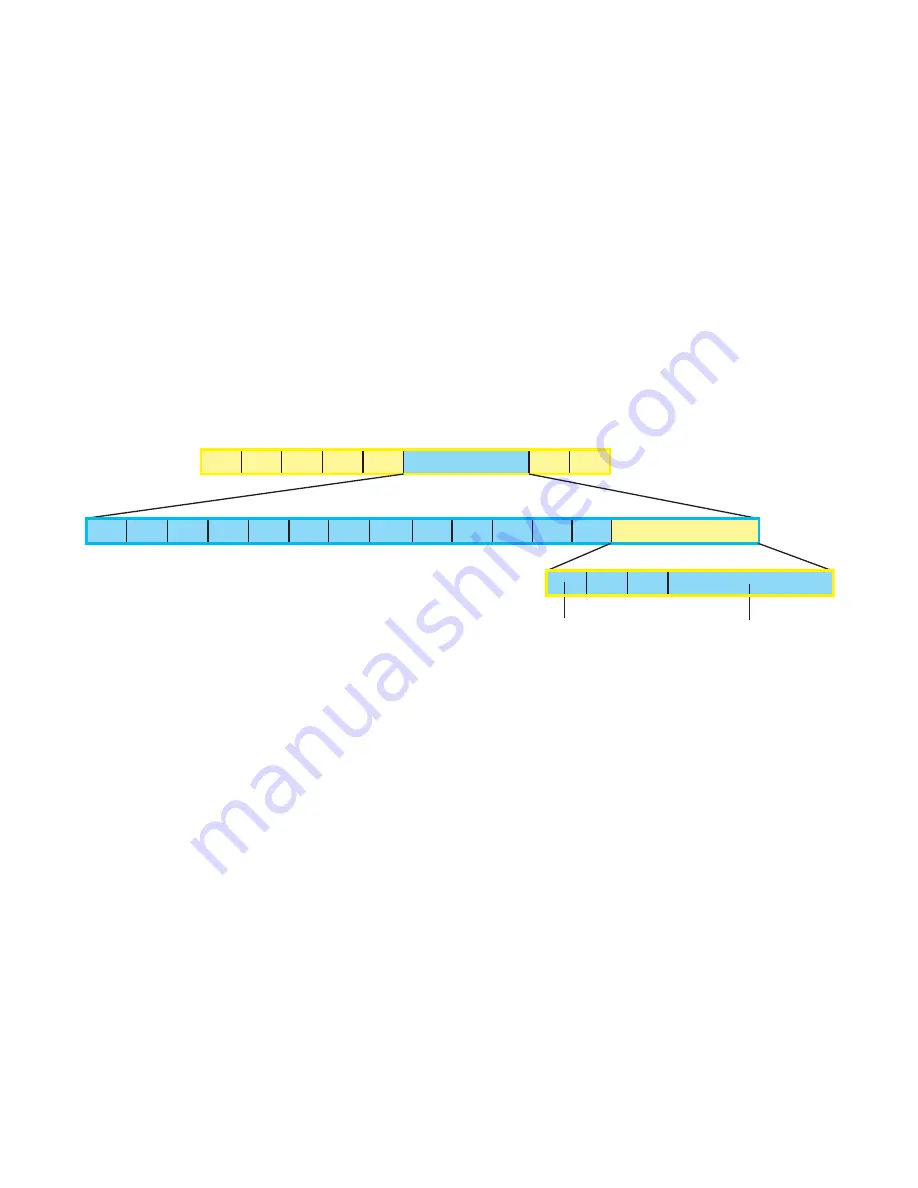
IGMP messages are encapsulated in IP packets, as shown in
Figure 19-1
.
Figure 19-1. IGMP version 2 Packet Format
Joining a Multicast Group
There are two ways that a host may join a multicast group: it may respond to a general query from its
querier, or it may send an unsolicited report to its querier.
Responding to an IGMP Query
1. One router on a subnet is elected as the querier. The querier periodically multicasts (to
all-multicast-systems address 224.0.0.1) a general query to all hosts on the subnet.
2. A host that wants to join a multicast group responds with an IGMP Membership Report that contains
the multicast address of the group it wants to join (the packet is addressed to the same group). If
multiple hosts want to join the same multicast group, only the report from the first host to respond
reaches the querier, and the remaining hosts suppress their responses (see
Adjusting Query and
Response Timers on page 410
for how the delay timer mechanism works).
3. The querier receives the report for a group and adds the group to the list of multicast groups associated
with its outgoing port to the subnet. Multicast traffic for the group is then forwarded to that subnet.
Version
(4)
IHL
TOS
(0xc0)
Total Length
Flags
Frag Offset
IGMP Packet
Header
Checksum
Src IP Addr
TTL
(1)
Protocol
(2)
Dest IP Addr
Options
(Router Alert)
Padding
Preamble
Start Frame
Delimiter
Destination MAC
Source MAC
Ethernet Type
IP Packet
Padding
fnC0069mp
Type
Max. Response
Time
Group Address
Checksum
Code: 0x11: Membership Query
0x12: IGMP version 1 Membership Report
0x16: IGMP version 2 Membership Report
0x17: IGMP Leave Group
8 bits
16 bits
May be zero and ignored by hosts for
general queries or contain a group
address for group-specific queries
FCS
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...