214
|
Border Gateway Protocol IPv4 (BGPv4)
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Weight
The Weight attribute is local to the router and is not advertised to neighboring routers. If the router learns
about more than one route to the same destination, the route with the highest weight will be preferred. The
route with the highest weight is installed in the IP routing table.
Local Preference
Local Preference (LOCAL_PREF) represents the degree of preference within the entire AS. The higher the
number, the greater the preference for the route.
The Local Preference (LOCAL_PREF) is one of the criteria used to determine the best path, so keep in
mind that other criteria may impact selection, as shown in
Figure 10-4
. For this example, assume that
LOCAL_PREF is the only attribute applied. In
Figure 10-5
, AS100 has two possible paths to AS 200.
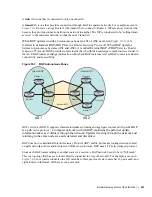
Although the path through the Router A is shorter (one hop instead of two) the LOCAL_PREF settings
have the preferred path go through Router B and AS300. This is advertised to all routers within AS100
causing all BGP speakers to prefer the path through Router B.
Figure 10-5. LOCAL_PREF Example
Multi-Exit Discriminators (MEDs)
If two Autonomous Systems (AS) connect in more than one place, a Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) can
be used to assign a preference to a preferred path. The MED is one of the criteria used to determine the best
path, so keep in mind that other criteria may impact selection, as shown in
Figure 10-4
.
Router A
Router B
AS 100
Router C
T1 Link
OC3 Link
AS 200
Router D
Router E
AS 300
Router F
Router E
Set Local Preference to 200
Set Local Preference to 100
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...