Bidirectional Forwarding Detection |
173
BFD sessions
BFD must be enabled on both sides of a link in order to establish a session. The two participating systems
can assume either of two roles:
•
Active
—The active system initiates the BFD session. Both systems can be active for the same session.
•
Passive
—The passive system does not initiate a session. It only responds to a request for session
initialization from the active system.
A BFD session has two modes:
•
Asynchronous mode
—In Asynchronous mode, both systems send periodic control messages at an
agreed upon interval to indicate that their session status is Up.
•
Demand mode
—If one system requests Demand mode, the other system stops sending periodic
control packets; it only sends a response to status inquiries from the Demand mode initiator. Either
system (but not both) can request Demand mode at any time.
A session can have four states: Administratively Down, Down, Init, and Up.
•
Administratively Down
—The local system will not participate in a particular session.
•
Down
—The remote system is not sending any control packets or at least not within the detection time
for a particular session.
•
Init
—The local system is communicating.
•
Up
—The both systems are exchanging control packets.
The session is declared down if:
•
A control packet is not received within the detection time.
•
Sufficient echo packets are lost.
•
Demand mode is active and a control packet is not received in response to a poll packet.
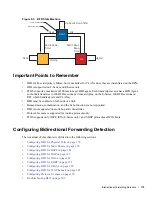
BFD three-way handshake
A three-way handshake must take place between the systems that will participate in the BFD session. The
handshake shown in
Figure 9-2
assumes that there is one active and one passive system, and that this is the
first session established on this link. The default session state on both ports is Down.
1. The active system sends a steady stream of control packets that indicates that its session state is Down,
until the passive system responds. These packets are sent at the desired transmit interval of the Active
system, and the Your Discriminator field is set to zero.
2. When the passive system receives any of these control packets, it changes its session state to Init, and
sends a response that indicates its state change. The response includes its session ID in the My
Discriminator field, and the session ID of the remote system in the Your Discriminator field.
3. The active system receives the response from the passive system, and changes its session state to Up. It
then sends a control packet indicating this state change. This is the third and final part of of the
Note:
FTOS supports asynchronous mode only.
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...