Intermediate System to Intermediate System |
507
23
Intermediate System to Intermediate System
Intermediate System to Intermediate System
is supported on platform:
e
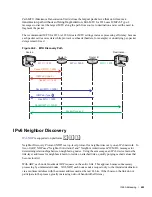
Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that
uses a shortest-path-first algorithm. Dell Force10 supports both IPv4 and IPv6 versions of IS-IS, as
described in this chapter.
•
Protocol Overview on page 507
•
IS-IS Addressing on page 508
•
Multi-Topology IS-IS on page 509
•
Graceful Restart on page 510
•
Implementation Information on page 511
•
Configuration Information on page 512
•
IS-IS Metric Styles on page 531
•
Sample Configuration on page 535
IS-IS protocol standards are listed in the
Appendix 63, Standards Compliance
chapter.
Protocol Overview
The intermediate-system-to-intermediate-system (IS-IS) protocol, developed by the International
Organization for Standardization (ISO), is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that uses a shortest-path-first
algorithm.
IS-IS is organized hierarchally into routing domains, and each router or system resides in at least one area.
In IS-IS, routers are designated as Level 1, Level 2 or Level 1-2 systems. Level 1 routers only route traffic
within an area, while Level 2 routers route traffic between areas. At its most basic, Level 1 systems route
traffic within the area and any traffic destined for outside the area is sent to a Level 1-2 system. Level 2
systems manage destination paths for external routers. Only Level 2 routers can exchange data packets or
Note:
This protocol supports routers passing both IP and OSI traffic, though the Dell Force10
implementation supports only IP traffic.
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...