Internet Group Management Protocol |
405
Sending an Unsolicited IGMP Report
A host does not have to wait for a general query to join a group. It may send an unsolicited IGMP
Membership Report, also called an IGMP Join message, to the querier.
Leaving a Multicast Group
1. A host sends a membership report of type 0x17 (IGMP Leave message) to the all routers multicast
address 224.0.0.2 when it no longer cares about multicast traffic for a particular group.
2. The querier sends a Group-Specific Query to determine whether there are any remaining hosts in the
group. There must be at least one receiver in a group on a subnet for a router to forward multicast
traffic for that group to the subnet.
3. Any remaining hosts respond to the query according to the delay timer mechanism (see
Adjusting
Query and Response Timers on page 410
). If no hosts respond (because there are none remaining in
the group) the querier waits a specified period, and sends another query. If it still receives no response,
the querier removes the group from the list associated with forwarding port and stops forwarding
traffic for that group to the subnet.
IGMP version 3
Conceptually, IGMP version 3 behaves the same as version 2. There are differences:
•
Version 3 adds the ability to filter by multicast source, which helps multicast routing protocols avoid
forwarding traffic to subnets where there are no interested receivers.
•
To enable filtering, routers must keep track of more state information, that is, the list of sources that
must be filtered. An additional query type, the Group-and-Source-Specific Query, keeps track of state
changes, while the Group-Specific and General queries still refresh existing state.
•
Reporting is more efficient and robust: hosts do not suppress query responses (non-suppression helps
track state and enables the immediate-leave and IGMP Snooping features), state-change reports are
retransmitted to insure delivery, and a single membership report bundles multiple statements from a
single host, rather than sending an individual packet for each statement.
The version 3 packet structure is different from version 2 to accommodate these protocol enhancements.
Queries (
Figure 19-2
) are still sent to the all-systems address 224.0.0.1, but reports (
Figure 19-3
) are sent
to the all IGMP version 3-capable multicast routers address 244.0.0.22.
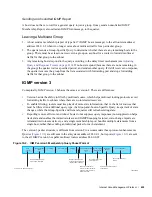
Figure 19-2. IGMP version 3 Membership Query Packet Format
fnC0070mp
Type
(0x11)
Max. Response
Code
Group Address
Checksum
Code: 0x11: Membership Query
Maximum Response Time
derived from this value
Reserved
S
Querier Robustness
Value
(2)
Querier's Query
Interval Code
Number of
Sources
Source Addresses
Bit flag that when set to
1 suppresses router query
response timer updates
Number of times that a
router or receiver transmits
a query or report to insure
that it is received
Query Interval derived
from this value
Number of source addresses
to be filtered
Source addresses to be
filtered
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...