Border Gateway Protocol IPv4 (BGPv4) |
209
In order to make decisions in its operations with other BGP peers, a BGP peer uses a simple finite state
machine that consists of six states: Idle, Connect, Active, OpenSent, OpenConfirm, and Established. For
each peer-to-peer session, a BGP implementation tracks which of these six states the session is in. The
BGP protocol defines the messages that each peer should exchange in order to change the session from one
state to another.
The first state is the
Idle
mode. BGP initializes all resources, refuses all inbound BGP connection attempts,
and initiates a TCP connection to the peer.
The next state is
Connect
. In this state the router waits for the TCP connection to complete, transitioning
to the
OpenSent
state if successful.
If that transition is not successful, BGP resets the ConnectRetry timer and transitions to the
Active
state
when the timer expires.
In the
Active
state, the router resets the ConnectRetry timer to zero, and returns to the
Connect
state.
Upon successful
OpenSent
transition, the router sends an Open message and waits for one in return.
Keepalive
messages are exchanged next, and upon successful receipt, the router is placed in the
Established
state. Keepalive messages continue to be sent at regular periods (established by the Keepalive
timer) to verify connections.
Once established, the router can now send/receive Keepalive, Update, and Notification messages to/from
its peer.
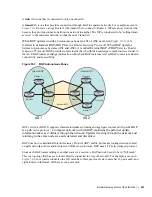
Peer Groups
Peer Groups are neighbors grouped according to common routing policies. They enable easier system
configuration and management by allowing groups of routers to share and inherit policies.
Peer groups also aid in convergence speed. When a BGP process needs to send the same information to a
large number of peers, it needs to set up a long output queue to get that information to all the proper peers.
If they are members of a peer group, however, the information can be sent to one place then passed onto
the peers within the group.
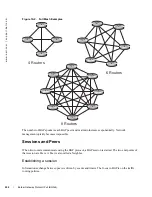
Route Reflectors
Route Reflectors reorganize the iBGP core into a hierarchy and allows some route advertisement rules.
Route reflection divides iBGP peers into two groups: client peers and nonclient peers. A route reflector and
its client peers form a route reflection cluster. Since BGP speakers announce only the best route for a given
prefix, route reflector rules are applied after the router makes its best path decision.
•
If a route was received from a nonclient peer, reflect the route to all client peers.
•
If the route was received from a client peer, reflect the route to all nonclient and all client peers.
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...