Open Shortest Path First (OSPFv2 and OSPFv3) |
697
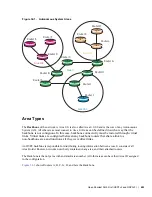
Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)
A Link-State Advertisement (LSA) communicates the router's local routing topology to all other local
routers in the same area.
•
OSPFv3 can treat LSAs as having link-local flooding scope, or store and flood them as if they are
understood, while ignoring them in their own SPF algorithms.
•
OSPFv2 always discards unknown LSA types.
The LSA types supported by Force 10 are defined as follows:
•
Type 1 - Router LSA
•
The router lists links to other routers or networks in the same area. Type 1 LSAs are flooded across
their own area only. The Link-State ID of the Type 1 LSA is the originating router ID.
•
Type 2 - Network LSA
•
The Designated Router (DR) in an area lists which routers are joined together within the area.
Type 2 LSAs are flooded across their own area only. The Link-State ID of the Type 2 LSA is the IP
interface address of the DR.
•
Type 3 - Summary LSA (OSPFv2), Inter-Area-Prefix LSA (OSPFv3)
•
An Area Border Router (ABR) takes information it has learned on one of its attached areas and can
summarize it before sending it out on other areas it is connected to. The Link-State ID of the Type
3 LSA is the destination network number.
•
Type 4 - AS Border Router Summary LSA (OSPFv2), Inter-Area-Router LSA (OSPFv3)
•
In some cases, Type 5 External LSAs are flooded to areas where the detailed next-hop information
may not be available. An Area Border Router will (ABR) flood the information for the router (i.e.
the Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) where the Type 5 advertisement originated. The
Link-State ID for Type 4 LSAs is the router ID of the described ASBR.
•
Type 5 - External LSA
•
These LSAs contain information imported into OSPF from other routing processes. They are
flooded to all areas, except stub areas. The Link-State ID of the Type 5 LSA is the external
network number.
•
Type 7
•
Routers in a Not-So-Stubby-Area (NSSA) do not receive external LSAs from Area Border Routers
(ABRs), but are allowed to send external routing information for redistribution. They use Type 7
LSAs to tell the ABRs about these external routes, which the Area Border Router then translates to
Type 5 external LSAs and floods as normal to the rest of the OSPF network.
•
Type 8 - Link LSA (OSPFv3)
•
This LSA carries the IPv6 address information of the local links.
•
Type 9 - Link Local LSA (OSPFv2), Intra-Area-Prefix LSA (OSPFv3)
•
For OSPFv2, this is a link-local “opaque” LSA as defined by RFC2370.
•
For OSPFv3, this LSA carries the IPv6 prefixes of the router and network links.
•
Type 11 - Grace LSA (OSPFv3)
•
For OSPFv3 only, this LSA is a link-local “opaque” LSA sent by a restarting OSPFv3 router
during a graceful restart.
Summary of Contents for Force10 E300
Page 1: ...FTOS Configuration Guide FTOS 8 4 2 7 E Series TeraScale C Series S Series S50 S25 ...
Page 32: ...32 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 132: ...132 802 1X w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 310: ...310 Configuration Replace and Rollback w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 330: ...330 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 402: ...402 High Availability w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 462: ...462 Interfaces w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 482: ...482 IPv4 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 506: ...506 IPv6 Addressing w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 582: ...582 Layer 2 w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 642: ...642 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 662: ...662 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 690: ...690 Object Tracking w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 754: ...754 PIM Dense Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 784: ...784 PIM Source Specific Mode w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 800: ...800 Power over Ethernet w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 876: ...876 Quality of Service w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 892: ...892 Routing Information Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1006: ...1006 Simple Network Management Protocol w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1018: ...1018 SONET SDH w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1048: ...1048 Broadcast Storm Control w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1096: ...1096 Uplink Failure Detection UFD w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1098: ...1098 Upgrade Procedures w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1196: ...1196 C Series Debugging and Diagnostics w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1252: ...1252 Standards Compliance w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...
Page 1262: ...1262 Index w w w d e l l c o m s u p p o r t d e l l c o m ...