B1: Continuouspath Mode, Exact Stop, LookAhead
3.2 Exact stop mode
Basic Functions
Function Manual, 09/2011, 6FC5397-0BP40-2BA0
151
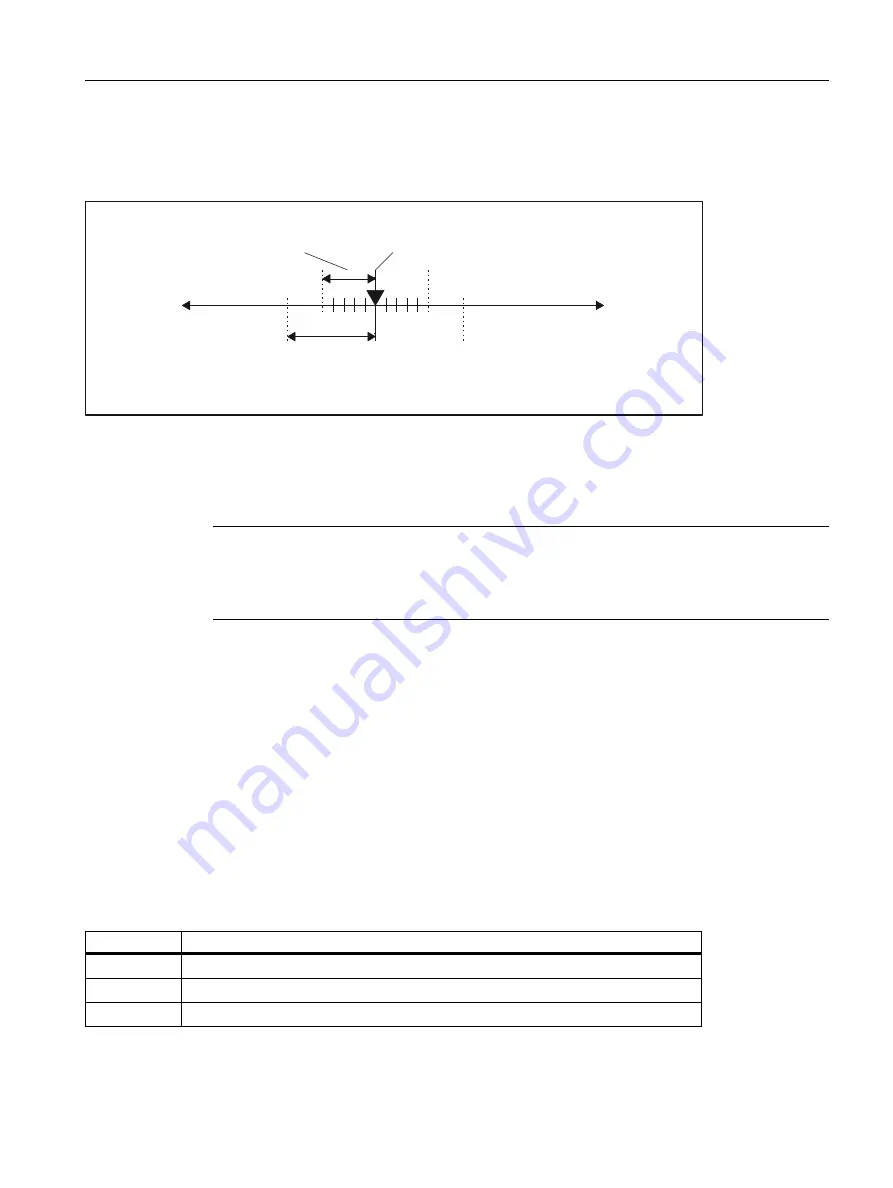
Exact stop criteria "Exact stop coarse" and "Exact stop fine".
The exact stop criteria "Exact stop coarse" and "Exact stop fine" are used to specify tolerance windows for a
machine axis reaching the "exact stop" state.
Figure 3-1
Tolerance windows of exact stop criteria
Parameters are assigned to the two exact stop criteria via the machine data:
MD36010 $MA_STOP_LIMIT_FINE (exact stop fine)
MD36000 $MA_STOP_LIMIT_COARSE (exact stop coarse)
Exact stop criterion "Interpolator End"
In the case of the exact stop criterion "interpolator end" the block change to the next traversing block takes place,
as soon as all path axes and special axes involved in the traversing motion, which do not traverse extending up
to block, have reached their position according to set point programmed in the block. That is, the interpolator has
executed the block.
The actual position and the following error of the relevant machine axes are not taken into consideration for exact
stop criterion "Interpolator end". Thus, depending on the dynamic response of the machine axes, this can result
in a relatively large smoothing of the contour at the block changes in comparison to the exact stop criteria "Exact
stop coarse" and "Exact stop fine".
Activation of an exact stop criterion
An exact stop criterion is activated in the part program by programming the appropriate G command:
Note
The tolerance windows of the exact stop criteria "Exact stop coarse" and "Exact stop fine"
should be assigned in such a way that the following requirement is fulfilled:
"Exact stop coarse" > "Exact stop fine"
G command
Exact-stop criterion
G601
Exact stop fine
G602
Exact stop coarse
G603
Interpolator end
6(7326,7,21
([DFWVWRSILQH
([DFWVWRS
FRDUVH
$[LVGLUHFWLRQ
QHJDWLYH
$[LVGLUHFWLRQ
SRVLWLYH
$&78$/326,7,21
















































