121
CHAPTER 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL
5
5.
2
List
of
P
a
ramet
e
rs
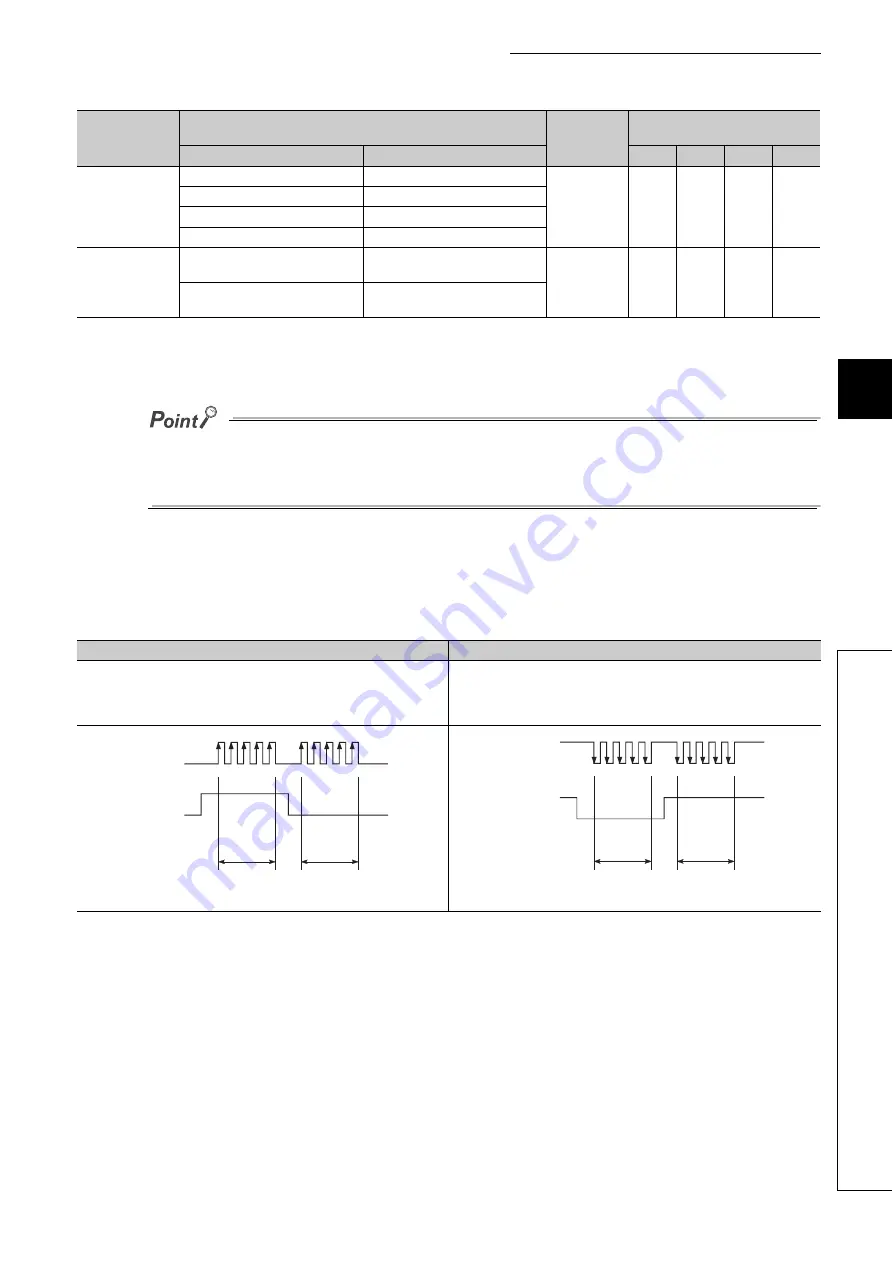
(5) [Pr.5] Pulse output mode
Set the pulse output mode to match the servo amplifier being used.
The only valid value of the "[Pr.5] Pulse output mode" is the value at the moment when the PLC READY signal [Y0] turns
from OFF to ON for the first time after the power is switched ON or the CPU module is reset. Once the PLC READY signal
[Y0] has been turned ON, the value will not be reset even if another value is set to the parameter and the PLC READY signal
[Y0] is turned from OFF to ON.
Use "[Pr.23] Output signal logic selection" to choose between the positive logic (pulse rising edge detection) and
negative logic (pulse falling edge detection). For the output specifications of each pulse output mode, refer to
An example of the pulse output mode for positive and negative logic is shown below.
(a) PULSE/SIGN mode
Item
Setting value, setting range
Default value
Setting value buffer memory
address
Value set with GX Works2
Value set with program
Axis 1
Axis 2
Axis 3
Axis 4
[Pr.5] Pulse output
mode
0:
PULSE/SIGN mode
0
1
4
154
304
454
1:
CW/CCW mode
1
2:
A phase/B phase (multiple of 4)
2
3:
A phase/B phase (multiple of 1)
3
[Pr.6] Rotation
direction setting
0:
Current value increment with
forward run pulse output
0
0
5
155
305
455
1:
Current value increment with
reverse run pulse output
1
Positive logic
Negative logic
Forward run and reverse run are controlled with the ON/OFF of the direction
sign (SIGN).
The motor will forward run when the direction sign is HIGH.
The motor will reverse run when the direction sign is LOW.
Forward run and reverse run are controlled with the ON/OFF of the direction
sign (SIGN).
The motor will forward run when the direction sign is LOW.
The motor will reverse run when the direction sign is HIGH.
The moving direction is + direction for forward run.
The moving direction is - direction for reverse run.
The moving direction is + direction for forward run.
The moving direction is - direction for reverse run.
Forward
run
Reverse
run
PULSE
SIGN
PULSE
SIGN
Forward
run
Reverse
run
Summary of Contents for MELSEC-L LD75D
Page 2: ......
Page 11: ...9 Memo ...
Page 176: ...174 ...
Page 264: ...262 ...
Page 266: ...264 ...
Page 267: ...265 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 268: ...266 ...
Page 269: ...267 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 270: ...268 ...
Page 271: ...269 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 272: ...270 Z ABRST1 instruction execution ...
Page 273: ...271 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 278: ...276 ...
Page 279: ...277 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 280: ...278 ...
Page 281: ...279 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 282: ...280 ...
Page 283: ...281 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 284: ...282 ...
Page 285: ...283 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 286: ...284 ...
Page 287: ...285 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 316: ...314 Memo ...
Page 685: ...683 APPENDICES A Appendix 1 Function Update Appendix 1 1 Function comparison Memo ...
Page 738: ...736 Memo ...
Page 817: ......
















































