535
CHAPTER 12 CONTROL SUB FUNCTIONS
12
12.
4
F
unct
ions
t
o Lim
it t
he
Cont
rol
12.4.3
Software stroke limit function
In the "software stroke limit function" the address established by a machine OPR is used to set the upper/lower limits of
the moveable range of the workpiece. Movement commands issued to addresses outside that setting range will not be
executed.
In the LD75, the "current feed value" and "machine feed value" are used as the addresses indicating the current
position. However, in the "software stroke limit function", the address used to carry out the limit check is designated in
the "[Pr.14] Software stroke limit selection". (Refer to
Page 353, Section 9.1.4 for details on the "current feed
value" and "machine feed value".)
The upper/lower limits of the moveable range of the workpiece are set in "[Pr.12] Software stroke limit upper limit
value"/ "[Pr.13] Software stroke limit lower limit value".
The details shown below explain about the "software stroke limit function".
• Differences in the moveable range when "current feed value" and "machine feed value" are selected.
• Software stroke limit check details
• Relation between the software stroke limit function and various controls
• Precautions during software stroke limit check
• Setting method
• Invalidating the software stroke limit
• Setting when the control unit is "degree"
(1) Differences in the moveable range when "current feed value" and "machine
feed value" are selected.
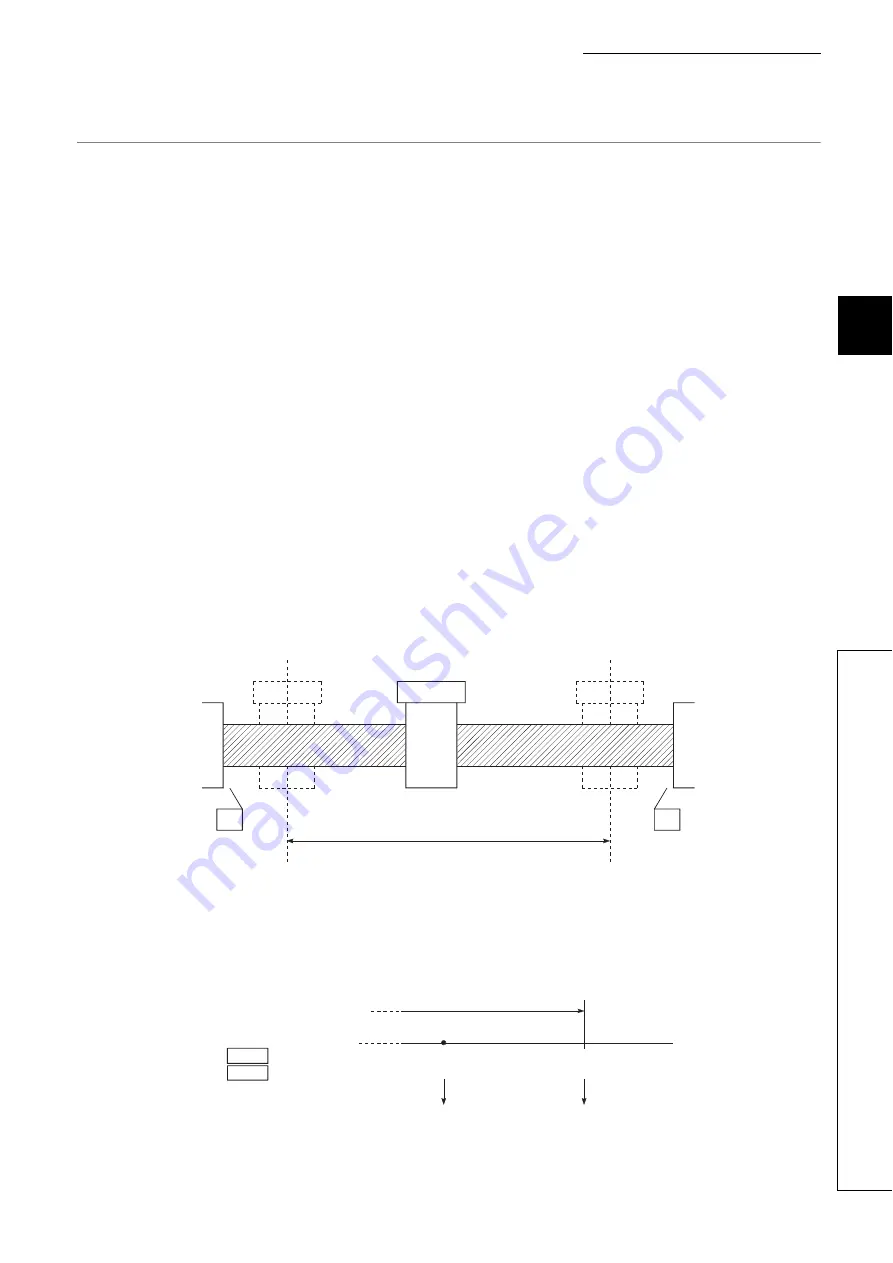
The following drawing shows the moveable range of the workpiece when the software stroke limit function is
used.
The following drawing shows the differences in the operation when "[Md.20] Current feed value" and "[Md.21]
Machine feed value" are used in the moveable range limit check.
[Condition]
Assume the current stop position is 2000, and the upper stroke limit is set to 5000.
FLS
RLS
Workpiece moveable range
Software stroke limit (lower limit)
Software stroke limit (upper limit)
5000
5000
Upper stroke limit
2000
2000
Stop position
Moveable range
Md. 20 Current feed value
Md. 21 Machine feed value
Summary of Contents for MELSEC-L LD75D
Page 2: ......
Page 11: ...9 Memo ...
Page 176: ...174 ...
Page 264: ...262 ...
Page 266: ...264 ...
Page 267: ...265 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 268: ...266 ...
Page 269: ...267 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 270: ...268 ...
Page 271: ...269 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 272: ...270 Z ABRST1 instruction execution ...
Page 273: ...271 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 278: ...276 ...
Page 279: ...277 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 280: ...278 ...
Page 281: ...279 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 282: ...280 ...
Page 283: ...281 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 284: ...282 ...
Page 285: ...283 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 286: ...284 ...
Page 287: ...285 CHAPTER 6 PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL 6 6 4 Positioning Program Examples ...
Page 316: ...314 Memo ...
Page 685: ...683 APPENDICES A Appendix 1 Function Update Appendix 1 1 Function comparison Memo ...
Page 738: ...736 Memo ...
Page 817: ......
















































