8 - 3 8 - 3
MELSEC-Q
8 OPR CONTROL
8.2.2 Machine OPR method
The method by which the machine OP is established (method for judging the OP
position and OPR completion) is designated in the machine OPR control according to
the configuration and application of the positioning control system.
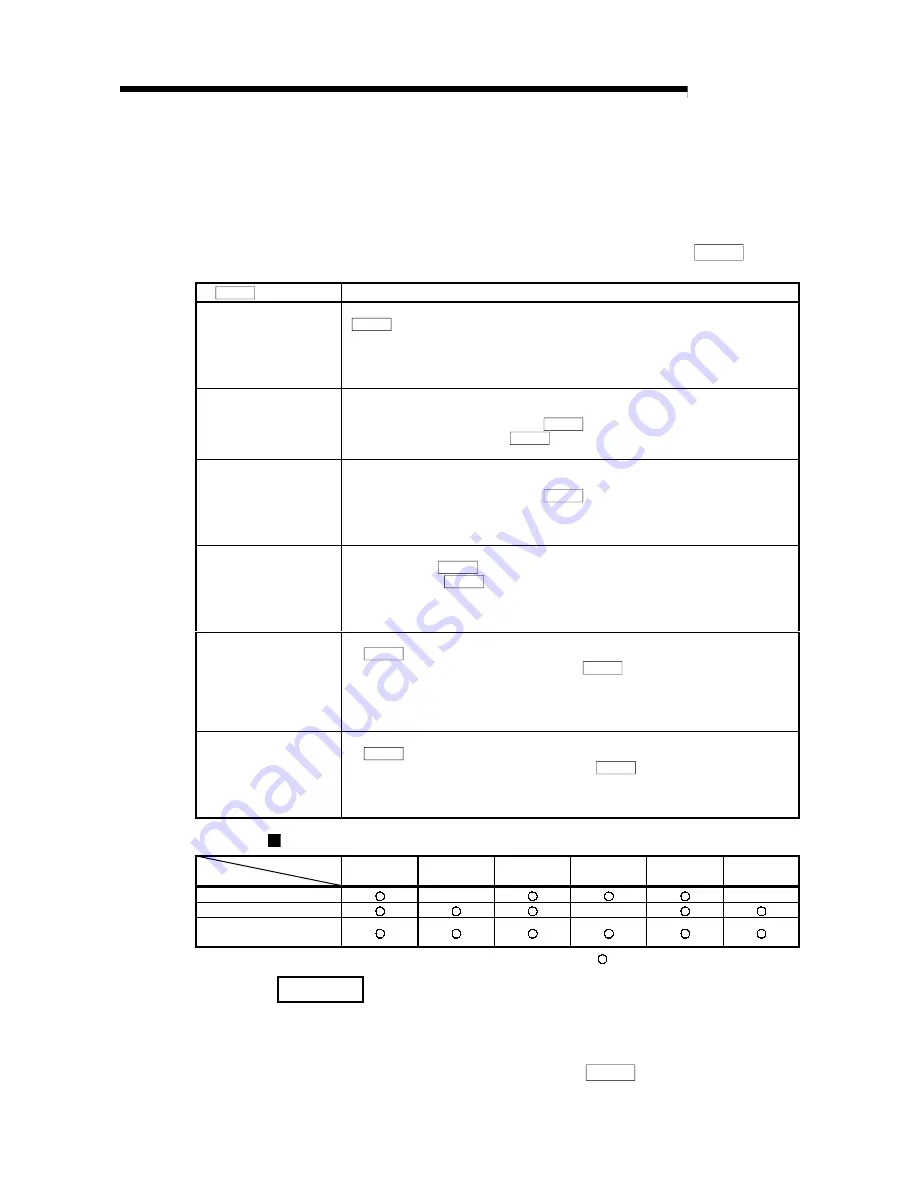
The following table shows the six methods that can be used for this OPR method.
(The OPR method is one of the items set in the OPR data. It is set in "OPR. 1 OPR
method" of the OPR data.)
OPR. 1 OPR method
Description
Near-point dog method
Deceleration starts when the near-point dog turns from OFF to ON. (Speed is decreased to
" OPR. 5 Creep speed")
The axis stops on detection of the first zero signal (one pulse of which is output when the
motor turns one revolution, e.g. Z-phase signal output from the drive unit) after the near-
point dog has turned from OFF to ON, and on completion of the deviation counter clear
output, OPR control is completed.
Stopper 1
The stopper position is defined as the OP.
After deceleration is started when the near-point dog turns from OFF to ON, the axis is
brought into contact with the stopper at " OPR. 5 Creep speed" to a stop.
After the stop, the time preset in " OPR. 9 OPR dwell time" elapses, and on completion of
the deviation counter clear output, OPR control is completed.
Stopper 2
The stopper position is defined as the OP.
After deceleration is started when the near-point dog turns from OFF to ON, the axis is
brought into contact with the stopper at " OPR. 5 Creep speed" to a stop.
After the stop, the zero signal (signal that is output on detection of contact with the stopper)
is detected, and on completion of the deviation counter clear output, OPR control is
completed.
Stopper 3
The stopper position is defined as the OP.
The axis starts at " OPR. 5 Creep speed" from the beginning, and is brought into contact
with the stopper at " OPR. 5 Creep speed" to a stop.
After the stop, the zero signal (signal that is output on detection of contact with the stopper)
is detected, and on completion of the deviation counter clear output, OPR control is
completed.
Count 1
Deceleration is started when the near-point dog turns from OFF to ON, and the axis moves
at " OPR. 5 Creep speed".
After the axis has moved the distance preset in "OPR. 8 Setting for the movement amount
after near-point dog ON" from the position where the near-point dog turned from OFF to
ON, it stops on detection of the zero signal (one pulse of which is output when the motor
rotates one revolution, e.g. Z-phase signal output from the drive unit), and on completion of
the deviation counter clear output, OPR control is completed.
Count 2
Deceleration is started when the near-point dog turns from OFF to ON, and the axis moves
at " OPR. 5 Creep speed".
The axis stops after moving the distance preset in " OPR. 8 Setting for the movement
amount after near-point dog ON" from the position where the near-point dog turned from
OFF to ON, and on completion of the deviation counter clear output, OPR control is
completed.
Wiring of signals required for each OPR method
OPR method
I/O signal
Near-point
dog method
Stopper 1
Stopper 2
Stopper 3
Count 1
Count 2
Zero signal (PG0)
–
–
Near-point dog (DOG)
–
Deviation counter clear
(CLEAR)
: Wiring required –: Wiring not required
REMARK
Creep speed
The stopping accuracy is poor when the machine suddenly stops from fast speeds.
To improve the machine's stopping accuracy, its must change over to a slow
speed before stopping. This speed is set in the "OPR. 5 Creep speed".
Summary of Contents for GX Configurator-PT
Page 13: ...MEMO SECTION 1...
Page 127: ...7 20 7 20 MELSEC Q 7 SEQUENCE PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 129: ...MEMO SECTION 2...
Page 221: ...Index 5 Index 5 MEMO...















































