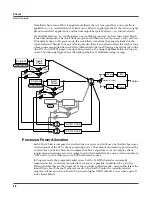
Effects
General Parameters
9-11
value is context-sensitive—in this example, the choices would be “Rvb->Cmp” and
“Cmp->Rvb”.
A/Dry->B
is also found in many combination algorithms, and controls the amount of signal that
will pass dry (unprocessed) through the first component into the second component. Different
combination algorithms use different variations on this parameter, depending on the context.
The range is 0 to 100%.
Reverbs
Room Type
changes the configuration of the algorithm to simulate a wide array of room types
and sizes including booths, small rooms, chambers, halls and large spaces. Because this
parameter changes the structure of the reverb algorithm, you need to be careful when assigning
it a MOD—changing it in real time while signal is passing through it is likely to cause audible
artifacts. Room types in different algorithms with similar names do not necessarily sound the
same.
Rvrb Time
is the RT
60
—the time it takes for the reverb to decay to 60 dB below its initial level—
in seconds. It is accurate assuming that several other parameters (HF Damping, Diff Scale, Size
Scale, and Density) are at their nominal levels. It is adjustable up to “Inf”, which creates an
infinitely-sustaining reverb.
LateRvbTim
adjusts the basic decay time of the late portion of the reverb after diffusion.
L/R Pre Dly
(Pre-Delay) is the time between the start of a sound and the output of the first
reverb reflections from that sound. Longer pre-delays can help make larger spaces sound more
realistic. Longer times can also help improve the clarity of a mix by separating the reverb signal
from the dry signal, so the dry signal is not obscured.
EarRef Lvl
adjusts the mix level of the early-reflection portion of algorithms which offer early
reflections.
Late Lvl
adjusts the mix level of the late-reverb portion of algorithms which offer early
reflections.
Diff Scale
scales the “diffusion“ of the early reflections, that is, how spread out they are as a
group over time. At very low settings, the early reflections start to sound quite discrete, and at
higher settings the early reflections are seamless. It is adjustable from 0.00 to 2.00, with 1.00
being nominal for the given Room Type.
Density
controls how tightly the early reflections are packed in time. Low Density settings
group the early reflections close together, while higher values spread the reflections for a
smoother reverb. It is adjustable from 0.00 to 4.00, with 1.00 being nominal (and usually optimal)
for the given Room Type.
Expanse controls the amount of late reverb energy biased toward the edges of the stereo image.
A setting of 0% will bias energy towards the center. Moving away from 0% will bias energy
towards the sides. Positive and negative values will have a different character.
Build adjusts the envelope of certain portions of the reverb. Positive values speed up the
envelope, and negative values slow it down.
Size Scale
changes the size of the current room. Altering this parameter will change the reverb
time and also cause some coloration of the reverb. It is adjustable from 0.00 to 4.00, with 1.00
being nominal (and usually optimal) for the given Room Type.
InfinDecay, when turned “On”, causes the reverb tail to decay indefinitely. When it’s “Off”, the
decay time is determined by the “Rvrb Time” or “LateRvbTim” parameters. This is a good
parameter to control with a footswitch.
Summary of Contents for PC3
Page 24: ...1 6 Introduction Options ...
Page 50: ...4 4 The Operating Modes Using the Modes ...
Page 174: ...7 54 Setup Mode The Utility Soft Buttons ...
Page 178: ...8 4 Quick Access Mode Making Your Own QA Banks ...
Page 204: ...9 26 Effects Mono Algorithms ...
Page 266: ...A 2 MIDI Implementation Chart ...
Page 308: ...Index x ...