Chapter
2:
Installation
The Standard Eclipse I/O Package
Eclipse User Guide
V1.0/1
31/ 380
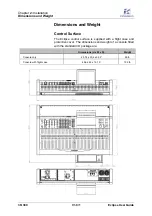
Console Rear Panel:
Every console is
always
fitted with the
DSP
and
MC
optical
cards:
DSP Card (with DIO interface)
This card provides the console’s internal DSP processing: 104
Input channels, 48 mix busses, 16 floating DSP paths and 48
assignable Delays.
It also includes 16 Line level balanced inputs, 16 balanced
outputs, and an Ethersound interface for connection to the
DioCore or external Ethersound device.
The card hosts 3 LEDs (
Sync
,
Prog
and
Pwr
) which indicate its
status.
There is also a BNC connector labeled
Sync out Dio
to clock
the console from an incoming Ethersound network (DioEs
module) in case where the console is not the primary master of
the Ethersound network (slave).
MC
optical
Card (Control and Sync)
This card handles control and synchronisation. It generates the
audio clocks, drives the digital bus, and handles
communications with the console’s integrated PC. The card
provides a choice of BNC or optical Receive and Transmit
connections to a remote StageBox if one is fitted. Note that a
Muxipaire Stagebox is an option on the Eclipse system. You
can find details on the Stagebox option on Page 240.
You will also find three connections for synchronisation:
•
Wc In
(BNC) – to connect an external Wordclock sync
reference.
•
Wc Out
(BNC) – Wordclock out. This output follows the
selected sync source and can be used to distribute
system clock to external devices.
•
AES In
(XLR) – to connect an external AES sync
reference.
You can find more details on clock signals on Page 41.
The headphone output (stereo ¼” jack) on the MC
optical
card is
left over from historical products and is not used on Eclipse.