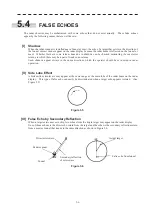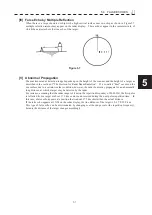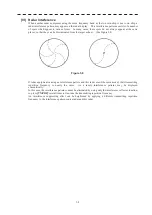
5.1 RADAR WAVE WITH THE HORIZON
yy
yyy
5-1
5
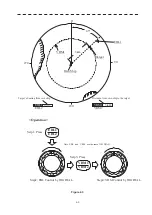
The radar operator has a role of interpreting the radar displays to provide his best aid in maneuvering the ship.
For this purpose, the operator has to observe the radar displays after fully understanding the advantages and
disadvantages that the radar has. For better interpretation of radar display, it is important to gain more
experiences by operating the radar equipment in fair weathers and comparing the target ships watched with the
naked eyes and their echoes on the radar display.
The radar is mainly used to monitor the courses of own ship and other ships in open seas, to check buoys and
other nautical marks when entering a port, to measure own ship’s position in the coastal waters relative to the
bearings and ranges of the shore or islands using a chart, and to monitor the position and movement of a heavy
rain if it appears on the radar display.
Various types of radar display will be explained below.
5.1
RADAR WAVE WITH THE HORIZON
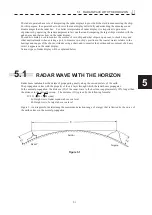
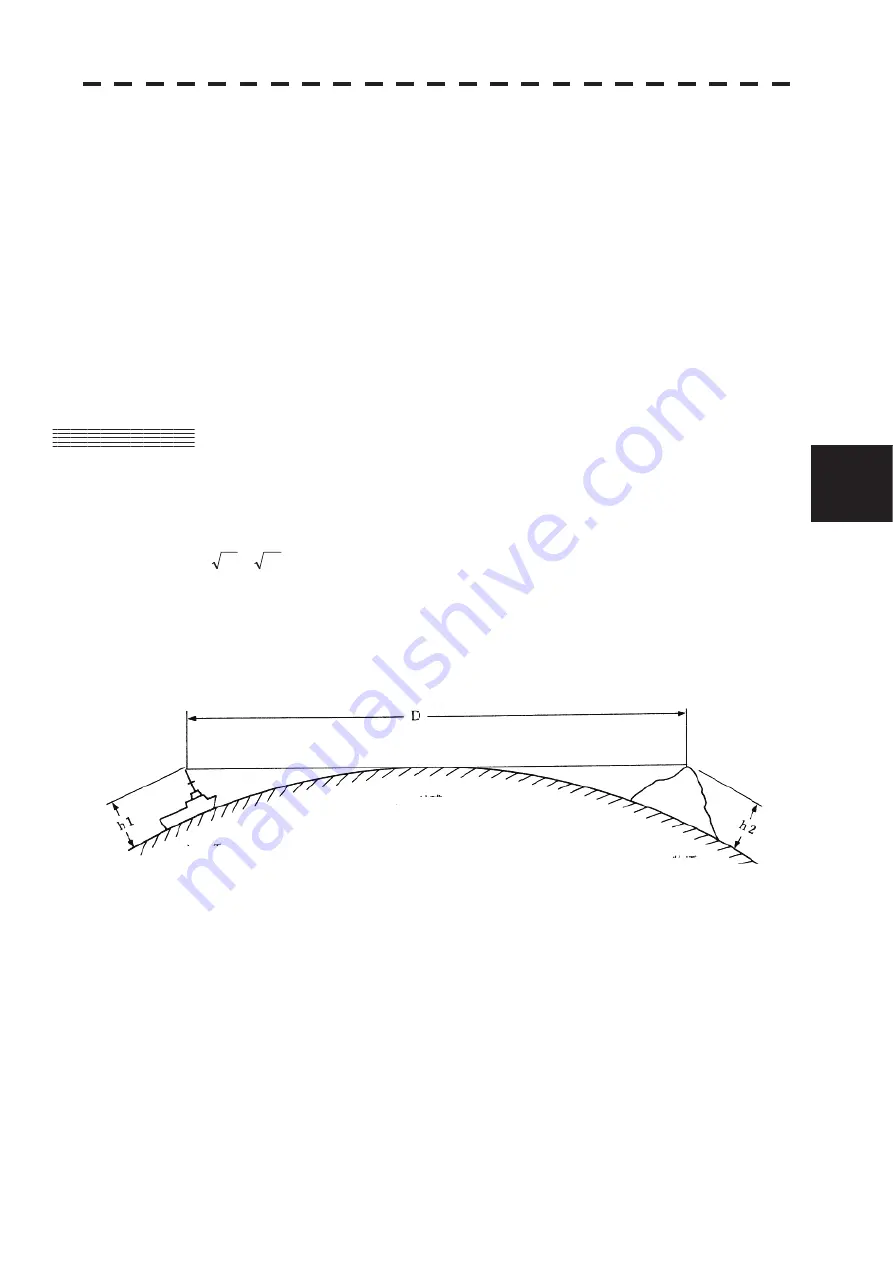
Radar beam radiation has the nature of propagating nearly along the curved surface of the earth.
The propagation varies with the property of the air layer through which the radar beam propagates.
In the normal propagation, the distance (D) of the radar wave to the horizon is approximately 10% longer than
the distance to the optical horizon. The distance (D) is given by the following formula:
D=2.23(
h2
h1
)(nm)
h1: Height (m) of radar scanner above sea level
h2: Height (m) of a target above sea level
Figure 5. is a diagram for determining the maximum detection range of a target that is limited by the curve of
the earth surface in the normal propagation.
Figure 5.1
Radar
Earth
Targets
Summary of Contents for JMR-611
Page 2: ......
Page 24: ......
Page 26: ......
Page 28: ......
Page 33: ...1 5 1 1 4 EXTERIOR DRAWINGS y Fig 1 1 Exterior Drawing of Scanner Unit Type NKE 387 Unit mm...
Page 34: ...1 6 Fig 1 2 Exterior Drawing of Processing Unit Type NDC 1774 Unit mm...
Page 35: ...1 7 1 1 4 EXTERIOR DRAWINGS y Fig 1 3 Exterior Drawing of Operating Unit Type NCE 5923 Unit mm...
Page 38: ......
Page 54: ......
Page 116: ......
Page 118: ......
Page 124: ......
Page 134: ......
Page 136: ......
Page 142: ......
Page 144: ......
Page 154: ......
Page 156: ......
Page 160: ......
Page 164: ......
Page 166: ......
Page 172: ......
Page 174: ......
Page 177: ...APPENDIX Fig 1 Block Diagram of JMR 611...
Page 181: ...APPENDIX Fig 5 Internal Connection Diagram of Control Unit NCM 994...
Page 182: ......
Page 184: ......
Page 186: ......
Page 187: ......