GE M
EDICAL
S
YSTEMS
D
IRECTION
FK091075, R
EVISION
04
V
IVID
3N P
RO
/E
XPERT
S
ERVICE
M
ANUAL
Chapter 5 Components and Function (Theory)
5-19
5-4-6
Beamformer Board (BF)
5-4-6-1
General Description
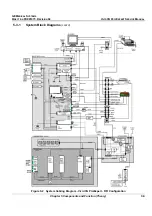
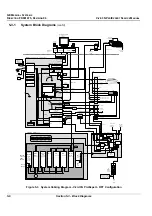
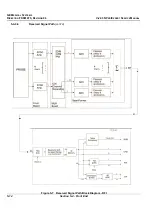
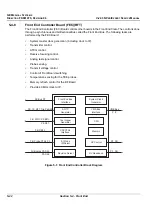
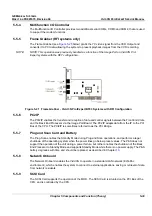
The Beamformer Board (BF Board) contains the A/D converter, the ASIC (called the Focuser [FOC])
and a Beam Adder (BA)
.
The BF Board accepts input channels and converts each channel to digital
bytes.
The system requires one BF Board which scans 64 channels.
The digitized samples at the ADC output are input to the FOCs, whose outputs go to a BA. The output
of the BA (BA Level 2) is the sum of the input channels, which is added together with the output from
the other BA Level 2, as shown in
Figure 5-12
on page 5-19.
These ASICs will add all the input and output channels, with appropriate delay, to give optimal receive
focusing and beam steering as a function of time. All focusing and steering parameters for a scan are
stored in VRAM on the BF Board. The output of the BF Board is a high-frequency digital Word update.
This output can be added to any successive board, if more channels are required.
•
BF Calibration:
The system has a calibration procedure for the BF Board, which sets the offset
voltage for the ADC on the BF Board. If the BF Board is replaced, the calibration procedure has to
be performed, as described in
Beamformer Calibration
on page 6 - 24.
•
BF Board Location:
The BF Board can be placed in the Front End Crate, in the third slot from
the left side.
5-4-6-2
Description of Operation
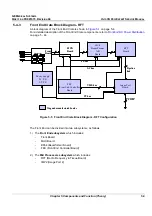
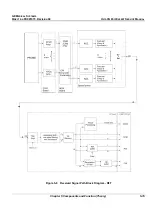
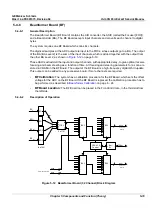
Figure 5-12 Beamformer Board (32 Channel) Block Diagram
AD C
AD C
AD C
AD C
From prev. board
To next
board
BA2
FE bus
21
21
12
Bus-
Ifc
RX
N
RX
N+1
RX
N+2
RX
N+3
(4 of 64)
FOC 2
0
1
BA2
BA2
BA2
(1 of 16)
SRAM &
Contro l
MLA0
To next
board
21
MLA1
MLA0
MLA1
21