Network Setup
4-135
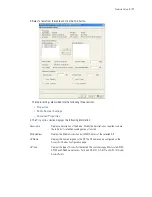
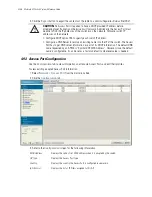
RTS Threshold
Specify a
Request To Send
(RTS) threshold (in bytes) for use by the WLAN's
adopted Access Ports.
RTS is a transmitting station's signal that requests a
Clear To Send
(CTS) response
from a receiving station. This RTS/CTS procedure clears the air where many MUs
(or nodes) are contending for transmission time. Benefits include fewer data
collisions and better communication with nodes that are hard to find (or hidden)
because of other active nodes in the transmission path.
Control RTS/CTS by setting an RTS threshold. This setting initiates an RTS/CTS
exchange for data frames larger than the threshold, and simply sends (without
RTS/CTS) any data frames that are smaller than the threshold.
Consider the trade-offs when setting an appropriate RTS threshold for the WLAN's
Access Ports. A lower RTS threshold causes more frequent RTS/CTS exchanges.
This consumes more bandwidth because of the additional latency (RTS/CTS
exchanges) before transmissions can commence. A disadvantage is the reduction
in data-frame throughput. An advantage is quicker system recovery from
electromagnetic interference and data collisions. Environments with more
wireless traffic and contention for transmission make the best use of a lower RTS
threshold.
A higher RTS threshold minimizes RTS/CTS exchanges, consuming less bandwidth
for data transmissions. A disadvantage is less help to nodes that encounter
interference and collisions. An advantage is faster data-frame throughput.
Environments with less wireless traffic and contention for transmission make the
best use of a higher RTS threshold. Default is 2346.
In 802.11b/g mixed RTS/CTS happens automatically. There is no way to disable
RTS/CTS unless the network and all the devices used are 802.11g or 802.11a only.
The proper co-existence of 802.11b and 802.11g is ensured through RTS/CTS
mechanism. On 802.11g radios CTS-to-self is enabled irrespective of whether or
not 11b rates are enabled or disabled.
When ERP Protection is ON, the 11bg radio will perform a CTS-to-self before it
transmits the frame.
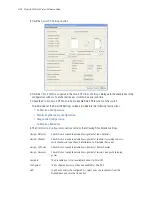
Beacon Interval
Specify a beacon interval in units of 1,000 microseconds (K-us). This is a multiple
of the DTIM value, for example, 100: 10. (See "DTIM Period" below). A beacon is
a packet broadcast by the adopted Access Ports to keep the network synchronized.
Included in a beacon is information such as the WLAN service area, the radio-port
address, the broadcast destination addresses, a time stamp, and indicators about
traffic and delivery such as a DTIM.
Increase the DTIM/beacon settings (lengthening the time) to let nodes sleep
longer and preserve battery life. Decrease these settings (shortening the time) to
support streaming-multicast audio and video applications that are jitter-sensitive.
Default is 100 K-us.
Summary of Contents for RFS Series
Page 1: ...M Motorola RFS Series Wireless LAN Switches WiNG System Reference Guide ...
Page 10: ...TOC 8 Motorola RF Switch System Reference Guide ...
Page 56: ...2 8 Motorola RF Switch System Reference ...
Page 334: ...5 52 Motorola RF Switch System Reference 2 Select the MU Status tab ...
Page 510: ...7 32 Motorola RF Switch System Reference Guide ...
Page 534: ...8 24 Motorola RF Switch System Reference Guide ...
Page 570: ...C 14 Motorola RF Switch System Reference Guide ...
Page 589: ......