Gated Clock Mode
MOTOROLA
Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
30-43
Figure 30-19. Network Mode Timing—Continuous Clock
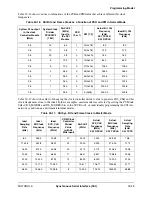
30.6 Gated Clock Mode
The gated clock mode is often used to connect to SPI-type interfaces on Microcontroller Units (MCUs) or
external peripheral chips. In gated clock mode, the presence of the clock indicates that valid data is on the
SSI_TXDAT or SSI_RXDAT pins. For this reason, no frame sync is needed in this mode. When
transmission of data is complete, the clock pin is tri-stated. Gated clocks are allowed for both the transmit
and receive sections with either internal or external clock and in Normal mode. Gated clocks are not
allowed in Network mode.
The clock runs when the TE bit or the RE bit in the SCSR are appropriately enabled. For clocks that are
generated internally, all internal bit clocks, word clocks, and frame clocks continue to operate. When a
valid time slot occurs, such as the first time slot in normal mode, the internal bit clock is enabled onto the
appropriate clock pin. This allows data to be transferred out in periodic intervals in gated clock mode.
When an external clock is used, the SSI waits for a clock signal to be received. When the clock begins,
valid data is shifted in.
For gated clock operation in external clock mode, a proper clock signal must be applied to the SSI STCK
for proper function. If the SSI uses a rising edge transition to clock data (TSCKP=0) and a falling edge
transition to latch data(RSCKP=0), the clock must be in an active low state when idle. If the SSI uses a
falling edge transition to clock data (TSCKP=1) and a rising edge transition to latch data (RSCKP=1), the
clock must be in an active high state when idle. The following diagrams illustrate the different edge
clocking and latching.
CLK
Frame Sync
STSR
TX DATA
SSI_TXDAT
TDE
TUE
SSI_RXDAT
RX DATA
RDR
ROE
0x5E
0xD6
0x7B
0x5E
0x5E
0xD6
0x7B
0x7B
0x5E
0x5E
0xD6
XX
XX
XX
0xD6
0x5E
0x5E
NOTE
: XX = “don’t care”
Summary of Contents for DragonBall MC9328MX1
Page 68: ...1 12 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Introduction ...
Page 86: ...2 18 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Signal Descriptions and Pin Assignments ...
Page 116: ...3 30 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Memory Map ...
Page 126: ...4 10 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA ARM920T Processor ...
Page 160: ...8 8 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA System Control ...
Page 272: ...13 32 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA DMA Controller ...
Page 281: ...Programming Model MOTOROLA Watchdog Timer Module 14 9 ...
Page 282: ...14 10 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Watchdog Timer Module ...
Page 300: ...15 18 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Analog Signal Processor ASP ...
Page 438: ...18 16 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Serial Peripheral Interface Modules SPI 1 and SPI 2 ...
Page 478: ...19 40 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA LCD Controller ...
Page 574: ...21 32 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Memory Stick Host Controller MSHC Module ...
Page 598: ...23 16 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Real Time Clock RTC ...
Page 670: ...24 72 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA SDRAM Memory Controller ...
Page 726: ...25 56 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA SmartCard Interface Module SIM ...
Page 736: ...26 10 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA General Purpose Timers ...
Page 854: ...29 18 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA I2C Module ...
Page 900: ...30 46 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA Synchronous Serial Interface SSI ...
Page 942: ...32 26 MC9328MX1 Reference Manual MOTOROLA GPIO Module and I O Multiplexer IOMUX ...