8 - 6
Chapter 8 OPR Control
8.2.2 Machine OPR method
The method by which the machine OP is established (method for judging the OP
position and machine OPR completion) is designated in the machine OPR according
to the configuration and application of the positioning method.
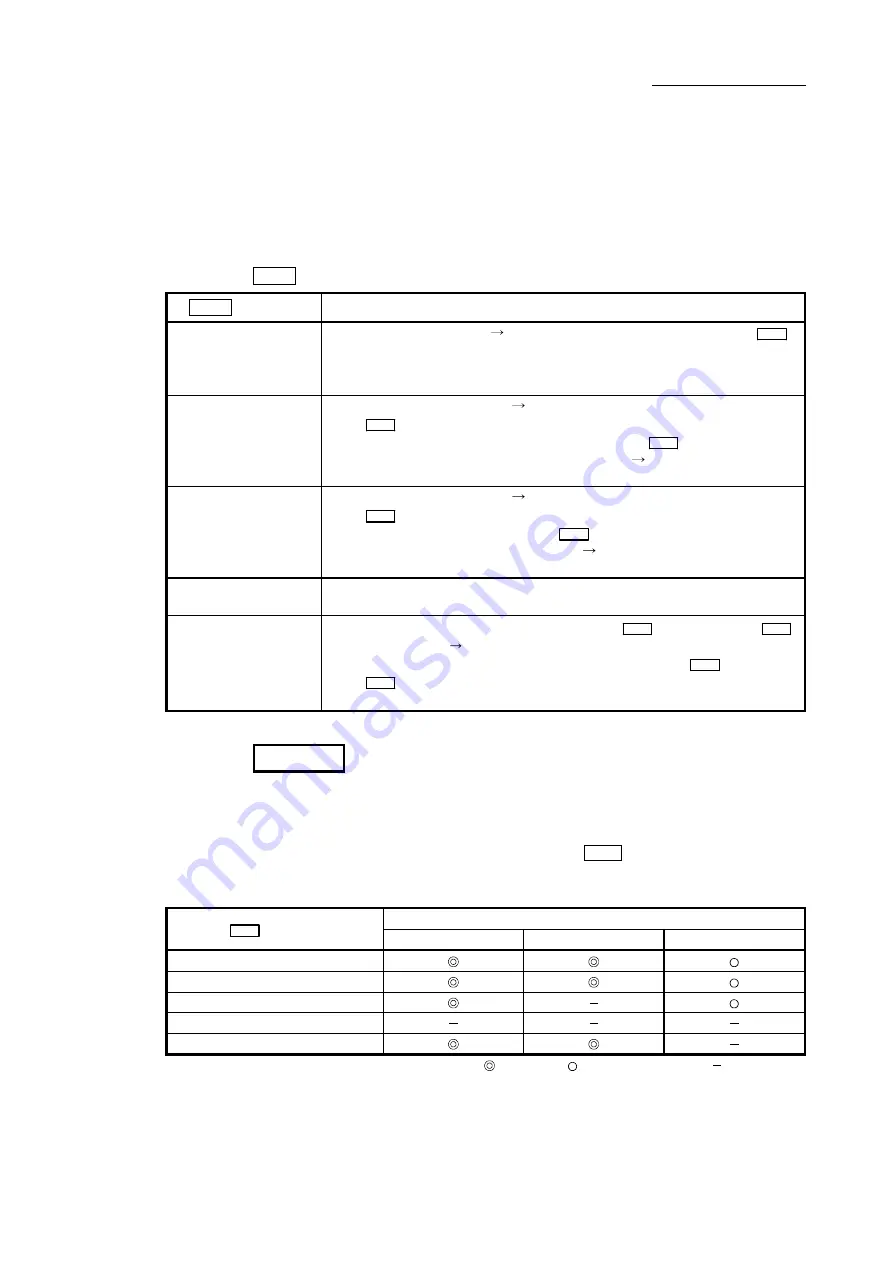
The following table shows the methods that can be used for this OPR method.
(The OPR method is one of the items set in the OPR parameters. It is set in
"
Pr.43
OPR method" of the basic parameters for OPR.)
Pr.43
OPR method
Operation details
Near-point dog method
Deceleration starts by the OFF ON of the near-point dog. (Speed is reduced to "
Pr.47
Creep speed".)
The operation stops once after the near-point dog turns ON and then OFF. Later the
operation restarts and then stops at the first zero signal to complete the OPR.
Count method 1)
The deceleration starts by the OFF ON of the near-point dog, and the machine moves
at the "
Pr.47
Creep speed".
The machine stops once after moving the distance set in the "
Pr.50
Setting for the
movement amount after near-point dog ON" from the OFF ON position. Later the
operation restarts and then stops at the first zero point to complete the machine OPR.
Count method 2)
The deceleration starts by the OFF ON of the near-point dog, and the machine moves
at the "
Pr.47
Creep speed.
The machine moves the distance set in the "
Pr.50
Setting for the movement amount after
near-point dog ON" from the near-point dog OFF ON position, and stops at that
position. The machine OPR is then regarded as completed.
Data set method
The position where the machine OPR has been performed becomes an OP.
The current feed value and feed machine value are overwritten to the OP address.
Scale origin signal
detection method
The machine moves in the opposite direction against of "
Pr.44
OPR direction
" at the "
Pr.46
OPR speed
" by the OFF ON of the near-point dog, and a deceleration stop is carried out
once at the first zero signal. Later the operation moves in direction of "
Pr.44
OPR direction
"
at the "
Pr.47
Creep speed
", and then stops at the detected nearest zero point to complete
the machine OPR.
REMARK
Creep speed
The stopping accuracy is poor when the machine suddenly stops from fast speeds.
To improve the machine's stopping accuracy, its must change over to a slow
speed before stopping. This speed is set in the "
Pr.47
Creep speed".
The following shows the signals as required for machine OPR.
Signals required for control
Pr.43
OPR method
Near-point dog
Zero signal
Upper/lower limit
Near-point dog method
Count method 1)
Count method 2)
Data set method
Scale origin signal detection method
: Necessary, : Necessary as required, : Unnecessary
Summary of Contents for MELSEC-Q QD77MS
Page 1: ......
Page 27: ...A 26 MEMO...
Page 29: ...MEMO...
Page 101: ...3 34 Chapter 3 Specifications and Functions MEMO...
Page 232: ...5 111 Chapter 5 Data Used for Positioning Control MEMO...
Page 315: ...5 194 Chapter 5 Data Used for Positioning Control MEMO...
Page 337: ...6 22 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 338: ...6 23 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 339: ...6 24 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 340: ...6 25 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 341: ...6 26 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 342: ...6 27 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 343: ...6 28 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 344: ...6 29 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 345: ...6 30 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 346: ...6 31 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 347: ...6 32 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 348: ...6 33 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 349: ...6 34 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 353: ...6 38 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 354: ...6 39 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 357: ...6 42 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 359: ...6 44 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 360: ...6 45 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 361: ...6 46 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 363: ...6 48 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 364: ...6 49 Chapter 6 Sequence Program Used for Positioning Control...
Page 413: ...MEMO...
Page 433: ...8 20 Chapter 8 OPR Control MEMO...
Page 458: ...9 25 Chapter 9 Major Positioning Control MEMO...
Page 593: ...10 30 Chapter 10 High Level Positioning Control MEMO...
Page 625: ...11 32 Chapter 11 Manual Control MEMO...
Page 659: ...12 34 Chapter 12 Expansion Control MEMO...
Page 767: ...13 108 Chapter 13 Control Sub Functions MEMO...
Page 813: ...14 46 Chapter 14 Common Functions MEMO...
Page 831: ...15 18 Chapter 15 Dedicated Instructions MEMO...
Page 846: ...16 15 Chapter 16 Troubleshooting MEMO...
Page 892: ...16 61 Chapter 16 Troubleshooting MEMO...
Page 971: ...Appendix 62 Appendices MEMO...
Page 974: ......
Page 975: ......
















































