68
Key Adjustments (Menus)
C
hap
te
r 4
K
eys
4
Carry out auto chroma key adjustments.
Also carry out manual adjustments (see next item), if
necessary, to obtain an optimum chroma key image.
5
In the <Mix Mode> group, select [Normal Mix] or
[Additive Mix] depending on the desired type of
chroma key composition.
When using an additive mix for chroma keying, the
(typically blue) background parts of the foreground video
must be converted to black. For this, use the color cancel
function
.
Using the plane function
In an additive mix, the foreground is not shaped by the key
signal, and variations in the (blue) background will appear
in the composite image. To prevent this, it is possible to set
a particular luminance level for the background, and any
parts below this level are cut forcibly.
1
In the Chroma Adjust menu, set [Plane] on.
2
Adjust the following parameters.
Key Adjustments (Menus)
This section describes key adjustments made using menu
operations.
You can adjust the following functions using menu
operations.
• Chroma Key Adjustment
• Masks
• Specifying the Key Output Destination
• Key Modify Clear
Chroma Key Adjustments
Methods of adjusting the composite obtained from chroma
keying include automatic adjustment with the auto chroma
key function, and manual adjustment carrying out the
necessary processing separately. The optimum results will
be obtained by first carrying out adjustments with the auto
chroma key function, then making any fine adjustments as
required.
The following manual adjustments are possible.
Key active
When this function is off, only the foreground is output
and you can make adjustments for color cancel (see the
next paragraph).
Color cancel
If the foreground image includes shades of the background
color, turn this function on to remove the color from the
foreground image.
Window
You can adjust the range over which the key signal is
determined as matching the specified hue. When this
function is off, the default range is used for the key.
Chroma keying generates a key signal based on a
particular color (reference color) in the foreground
(typically a plain blue background), and the “window”
refers to the range of colors which are regarded as
matching this specified reference color to create the key
signal.
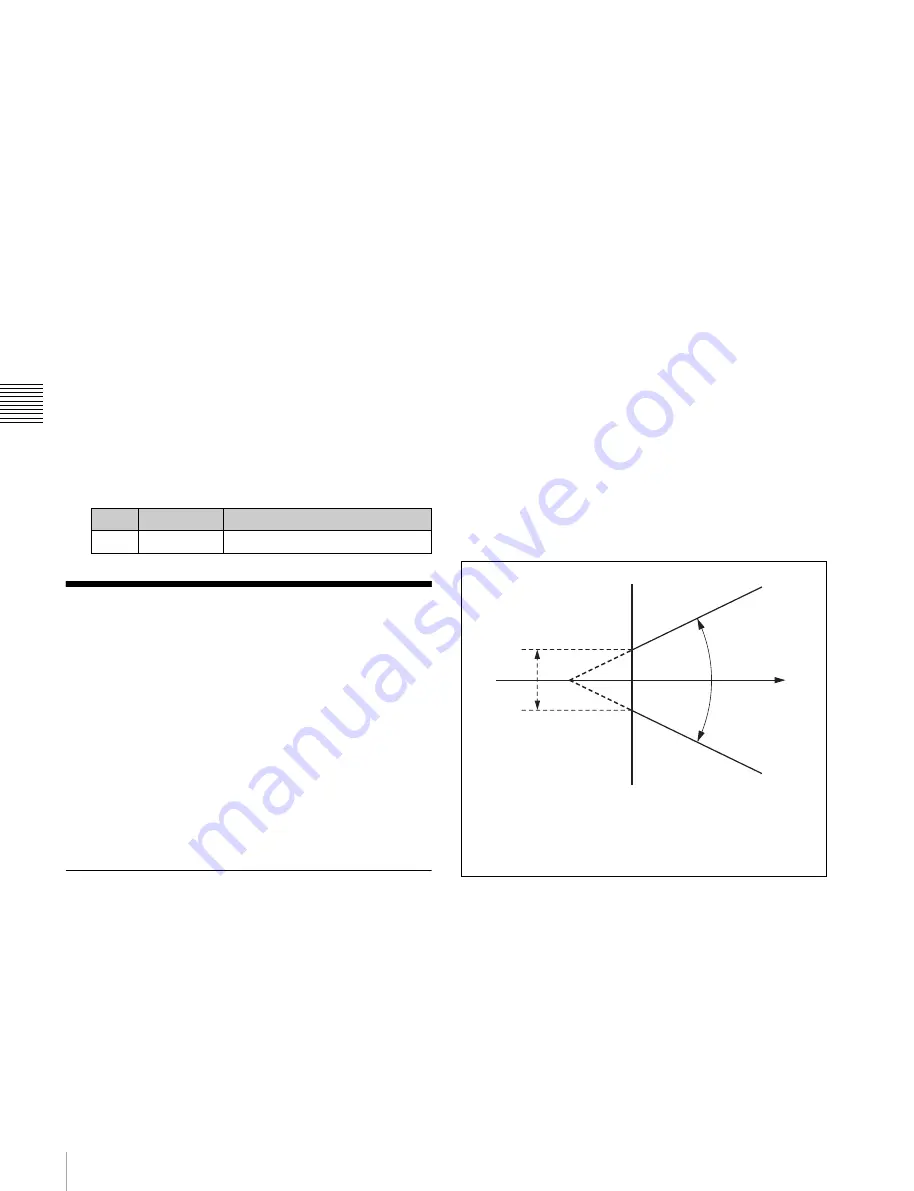
As seen on a vectorscope (that is, in the hue-saturation
color space), the range for this matching corresponds to a
truncated sector. This range is specified by two
parameters: the “Angle” parameter, which determines the
range of the hue parameter, and the “Crop” parameter,
which determines the degree of truncation (see the
following figure).
Y balance
In normal chroma keying, the key signal is generated from
the chrominance component only, and all elements of the
foreground with the same hue are replaced by the
background. Using the Y balance function, you can specify
a luminance level range within which the key is active, and
replace the specified part by the background.
You can use the Y balance function independently on the
key signal for the composition and the key signal for the
color cancel function. When applied to the key signal for
the composition, this produces the foreground with the
No.
Parameter
Adjustment
1
Luminance
Luminance level
Range of colors remaining
as foreground
Crop
a)
Reference
color
specified
by Hue
setting
Angle
a)
Range of colors creating the key
signal (to be replaced by
background signal)
a) The Crop and Angle values do not change even if you use
the auto chroma key function.






























