APPENDIX. HOST COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
IMR02E20-E1
139
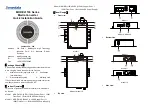
[Example] When performing control by calling up data in Memory area 3 of CH1
1.
The memory area number, “3” is written to the memory area transfer (08DCH).
Data in Memory area 3 is called up to the CH1 register addresses.
CH1 register addresses
Memory area transfer
08DCH
3
Memory area number, “3”
Event 1 set value (EV1)
095CH
Event 2 set value (EV2)
099CH
Event 3 set value (EV3)
09DCH
Event 4 set value (EV4)
0A1CH
Control loop break alarm (LBA) time
0A5CH
LBA deadband
0A9CH
Set value (SV)
0ADCH
Proportional band [heat-side]
0B1CH
Integral time [heat-side]
0B5CH
Derivative time [heat-side]
0B9CH
The data of memory area 3 is loaded into these register addresses.
Control response parameter
0BDCH
Proportional band [cool-side]
0C1CH
Integral time [cool-side]
0C5CH
Derivative time [cool-side]
0C9CH
Overlap/Deadband 0CDCH
Manual reset
0D1CH
Setting change rate limiter (up)
0D5CH
Setting change rate limiter (down)
0D9CH
Area soak time
0DDCH
Link area number 0E1CH
2.
Control of CH1 is performed by using data in the register addresses.
If the memory area transfer (08DCH to 091BH) and the setting memory area number
(386CH to 38ABH) are set to the same memory area number, the respective data can be
synchronized.
Values in the control areas (095CH to 0E5BH) and the setting memory area number
(38ACH to 3DABH) are set to the same memory area number, the respective data can
be synchronized.
If data in the control area is changed, data in the memory area is also changed.
If data in the memory area is changed, data in the control area is also changed.
Data mapping function
When using a COM-ML joined to function modules, the data mapping function cannot be used.