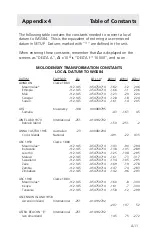
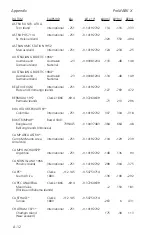
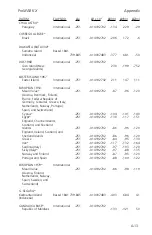
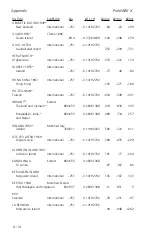
A-5
Appendix
ProMARK X
Appendix 2
DIFFERENTIAL THEORY
Differential positioning is a technique that allows you to overcome the
effects of environmental errors and Selective Availability (SA) on the GPS
signals to produce a highly accurate position fix. This is done by determining
the amount of the positioning error and applying it to position fixes that were
computed from collected data.
Typically, the horizontal accuracy of a single position fix from a GPS receiver
is 15 meters RMS (root-mean-square) or better. If the distribution of fixes
about the true position is circular normal with zero mean, an accuracy of 15
meters RMS implies that about 63% of the fixes obtained during a session
are within 15 meters of the true position.
There are two types of positioning errors; correctable and non-correctable.
Correctable errors are the errors that are essentially the same for two GPS
receivers in the same area. Non-correctable errors cannot be correlated
between two GPS receivers in the same area.
Correctable Errors
Sources of correctable errors include satellite clock, ephemeris data, and
ionospheric and tropospheric delay. If implemented, Selective Availability
may also cause a correctable positioning error.
Clock errors and ephemeris errors originate with the GPS satellite. A clock
error is a slowly changing error that appears as a bias on the pseudorange
measurement made by a receiver. An ephemeris error is a residual error in
the data used by a receiver to locate a satellite in space.
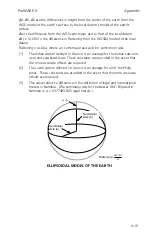
Ionospheric delay errors and tropospheric delay errors are caused by atmo-
spheric conditions. Ionospheric delay is caused by the density of electrons in
the ionosphere along the signal path. (The ionosphere is the upper portion
of the earth's atmosphere.) A tropospheric delay is related to humidity,
temperature, and altitude along the signal path. Usually, a tropospheric
error is smaller than an ionospheric error.
Another correctable error is caused by Selective Availability (SA). SA is used
by the United States Department of Defense to introduce errors into the
Standard Positioning Service (SPS) GPS signals to degrade fix accuracy. This
is done to maintain optimum military effectiveness by U.S. and allied forces.
Summary of Contents for GPS PROMARK X
Page 4: ......
Page 10: ...vi...
Page 14: ...Introduction ProMARK X 1 4...
Page 92: ...Attributes ProMARK X 6 8...
Page 188: ......