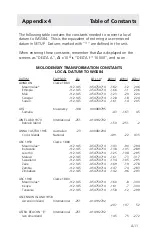
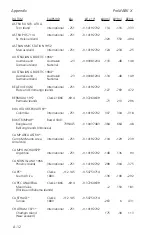
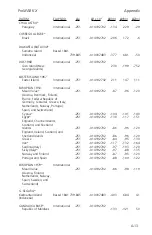
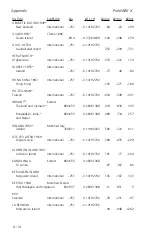
Appendix
ProMARK X
A-2
is programmed to ignore an unhealthy satellite and use the next
best satellite to obtain a position fix. Also, satellites are occa-
sionally taken off-line in order to do maintenance. A satellite
may also be taken off-line in order to move it to a new orbit
position.
How GPS Works
Each GPS satellite continuously broadcasts two signals: a Stan-
dard Positioning Service (SPS) signal for worldwide civilian use,
and a Precise Positioning Service (PPS) signal for U.S. and allied
military use. The SPS is a spread-spectrum signal broadcast at
1575.42 MHz. The signal is virtually resistant to multipath and
night-time interference, and is unaffected by weather and
electrical noise.
The SPS signal contains two types of orbit data: almanac and
ephemeris. Almanac data contains the health and approximate
location of every satellite in the system. A GPS receiver collects
almanac data from any available satellite, then uses it to locate
the satellites that should be visible at the receiver’s location.
Ephemeris data represents the precise orbital parameters of a
specific satellite.
The Global Positioning System
Summary of Contents for GPS PROMARK X
Page 4: ......
Page 10: ...vi...
Page 14: ...Introduction ProMARK X 1 4...
Page 92: ...Attributes ProMARK X 6 8...
Page 188: ......