Front Panel Operation
2-28
2.6.3 Current measurement considerations
Some considerations for making accurate current measure-
ments are summarized in the following paragraphs. Addi-
tional measurement considerations are summarized in
paragraph 2.21. For comprehensive information on precision
measurements, refer to the Low Level Measurements hand-
book, which is available from Keithley.
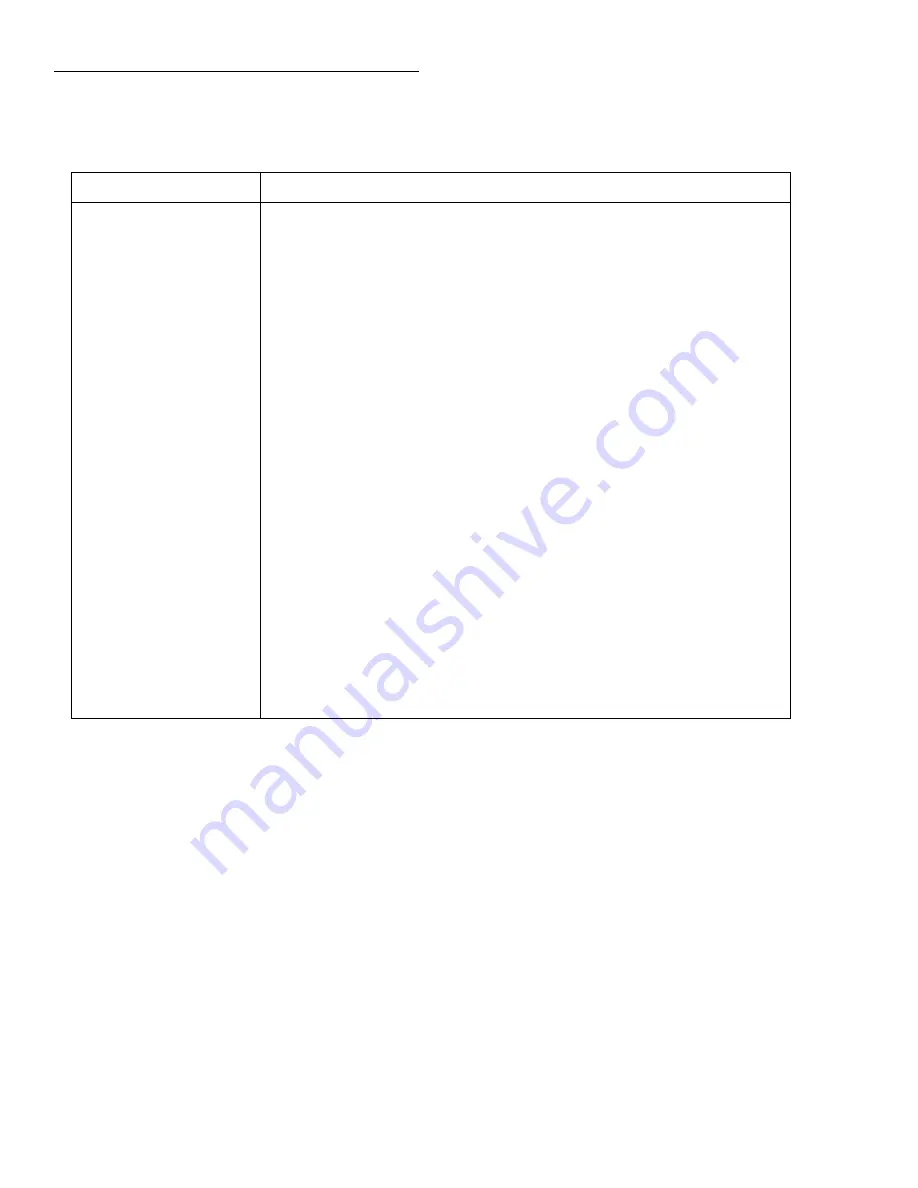
Table 2-9
CONFIGURE AMPS menu structure
Menu item
Description
SPEED
NORMAL
FAST
MEDIUM
HIACCURACY
SET-SPEED-EXACTLY
SET-BY-RSLN
Measurement speed (integration time) menu:
Select 1 PLC (power line cycle, 16.67msec for 60Hz, 20msec for 50Hz and 400Hz).
Select 0.01 PLC.
Select 0.1 PLC.
Select 10 PLC.
Set integration in PLC (0.01-10).
Default to setting appropriate for resolution.
FILTER
AVERAGING
TYPE
NONE
AVERAGING
ADVANCED
AVERAGING-MODE
MEDIAN
DISABLE
ENABLE
Filter menu:
Configure digital averaging filter:
Select type of average filter:
No average filtering performed.
Program a simple average filter (1-100 rdgs.).
Program a simple average filter (1-100 rdgs.) with noise tolerance window (0-
100% of range).
Select moving average or repeating average mode.
Configure median filter:
Disable median filter.
Enable median filter and specify rank (1-5).
RESOLUTION
AUTO
3.5d, 4.5d, 5.5d, 6.5d
Display resolution menu:
Default to resolution appropriate for integration time.
Select a specific resolution.
AUTO-RANGE
USE-ALL-RANGES
SET-LIMITS
MIN-AUTO
MAX-AUTO
Autorange menu:
Use all ranges when autoranging.
Limit the ranges used in the autorange search:
Specify the minimum range in the search.
Specify the maximum range in the search.
DAMPING
Enable or disable damping.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
An ideal ammeter would read 0A with an open input. In
practice, however, ammeters do have some current that flows
when the input is open. This current is known as the input
bias (offset) current and may be large enough to corrupt low
current measurements.
The input bias current for the Model 6517A is listed in the
specifications. Input bias current may be reduced by per-
forming the offset adjustment procedure explained in para-
graph 2.19.3 (OFFSET-ADJ).
















































