C
L E A R
P
A T H
M C / S D
U
S E R
M
A N U A L
R
E V
.
3 . 0 9
1 1 7
T
EKNIC
,
I
NC
. T
EL
.
(585)
784-7454
F
OLLOW
D
IGITAL
V
ELOCITY
C
OMMAND
(F
REQUENCY
I
NPUT
)
M
ODE
D
ESCRIPTION
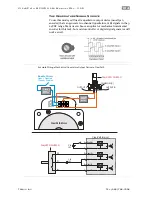
Connect a digital variable frequency waveform from your PLC or other
device, and ClearPath will run at a velocity proportional to the frequency
of the waveform.
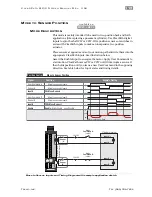
Assert the Enable Input to energize the motor. Then, control velocity by
applying a variable frequency pulse train to Input B. Pulse frequency is
proportional to commanded velocity. Direction of travel (CW/CCW) is
controlled by the state of Input A. See Inputs and Timing diagram below.
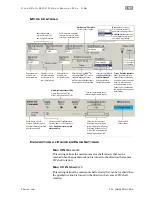
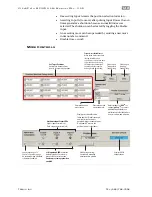
Signal
Function
Input Type
Input A
Motor velocity vs. time
Input B
Enable
Direction
Velocity
Enable
NA
NA
Trigger
Logic: High=CW Low=CCW
Pulse: Variable Frequency
Logic: High=Enable Low=Disable
0
1
0
1
t
v
Example Timing
Notes:
0
1
0
1
Follow Digital Velocity Command (Frequency Input Control)
Velocity Control
I/O
F
UNCTIONS
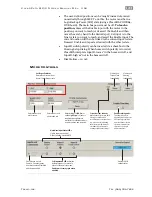
Enable Input -
Asserting this input energizes the motor shaft.
Input A -
This input selects the direction of rotation.
Input B -
This input is connected to a pulse train whose frequency
represents the desired speed.
Output (HLFB) -
See HLFB section for available modes.
Notes:
•
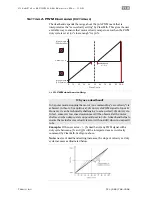
Input frequency range: 20 Hz to 700 kHz.
•
Actual motor speed in RPM is given by the following equation
[(Input Freq. - Min Freq.) / (Max Freq. - Min Freq.) * User
Defined Max Velocity. For
Example,
a 120 kHz pulse train
with 100 kHz Min Frequency and 200 kHz Max frequency will
result in a rotational speed of 20% of the user-defined Max
Velocity.
•
If the frequency signal is off/interrupted for 50mS or more the
input is considered off. This is interpreted by ClearPath as a
zero-velocity command.
•
Disable time = 10 mS
MCVC + MCPV
Available on