3-2
3
1. Outline of mode
Connection
Position Control Mode
Outline
You can perform position control based on the positional command (pulse train) from the
host controller.
This section describes the fundamental setup to be used for the position control.
Function
Caution
Note
(1) Process of command pulse input
The positional commands of the following 3 types (pulse train) are available.
• 2-phase pulse
• Positive direction pulse/negative direction pulse
• Pulse train + sign
Set the pulse configuration and pulse counting method based on the specification and
configuration of installation of the host controller.
The input terminals can accommodate the following 2 systems.
• Input 1 “PULSH1, PULSH2, SIGNH1, SIGNH2” line receiver input (4 Mpps)
• Input 2 “PULS1, PULS2, SIGN1, SIGN2” photocoupler input (500 kpps)
For line driver output, “Input 2” can also be used without changing the allowable input
frequency.
• Relevant parameters
Parameter
No.
Title
Range
Function
Pr0.05 Selection of command
pulse input
0 to 1
You can select either the photo-coupler input or the
exclusive input for line driver as the command pulse
input.
Pr0.06 Command pulse rotational
direction setup
0 to 1
Sets the counting direction when command pulse is
input.
Pr0.07 Command pulse input
mode setup
0 to 3
Sets the counting method when command pulse is
input.
For details of these parameters, refer to P.4-6 and 7 “Details of parameter”.
Related page
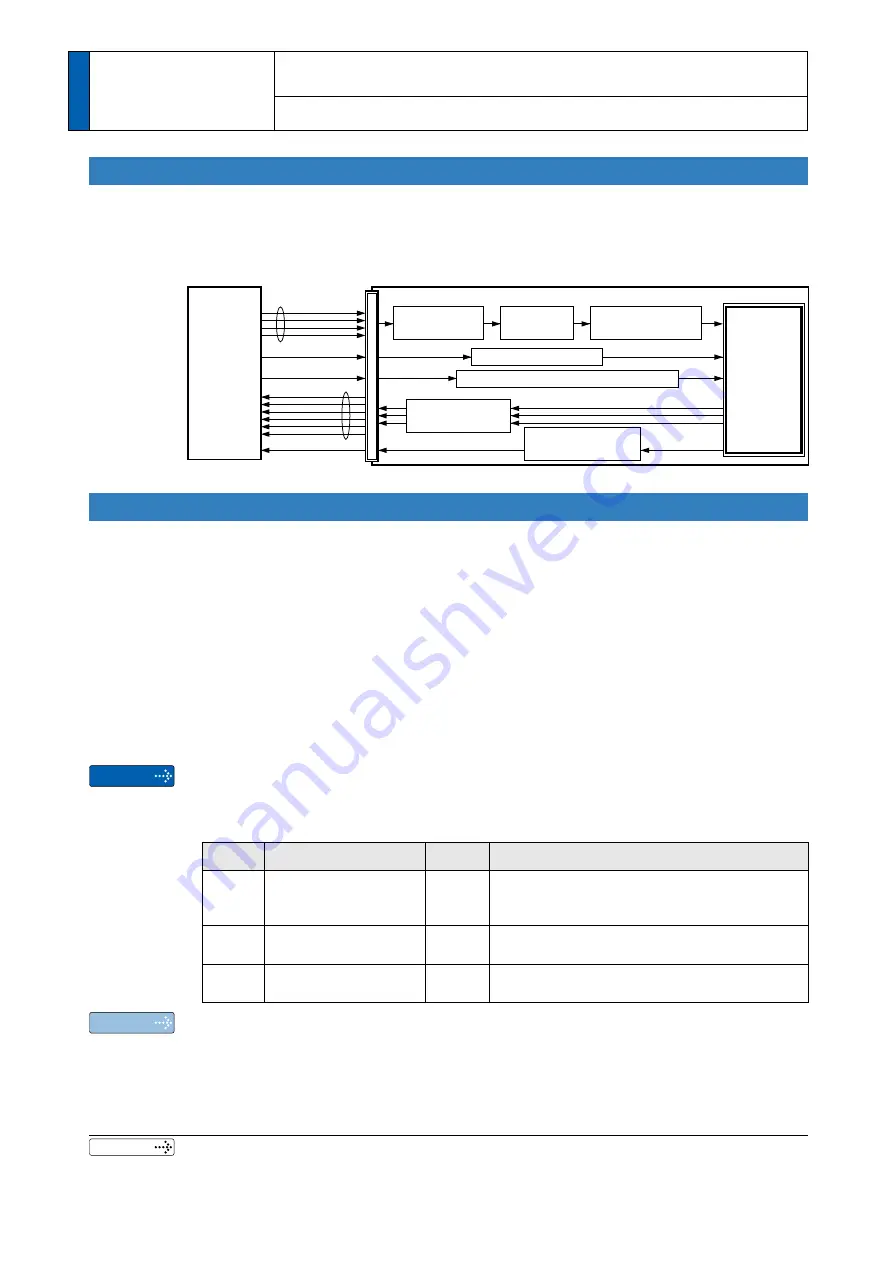
• P.3-14 “Control Block Diagram”
• P.3-18 “Wiring Diagram to the connector, X4”
Command pulse
input section
Pulse regeneration
function
Positioning complete
output (INP) function
Electronic
gear section
Positional command
filtering function
CL input
INP
output
Counter clear function
INH input
Pulse output
Command pulse inhibition (INH) function
Positional
command
(pulse train)
Servo driver
Host
controller
Position
control
section
Summary of Contents for MINAS A5-series
Page 36: ...1 24 MEMO ...
Page 118: ...2 82 MEMO ...
Page 168: ...3 50 MEMO ...
Page 272: ...5 42 MEMO ...
















































