M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
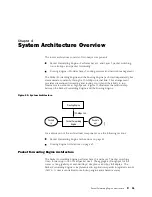
The Packet Forwarding Engine architecture includes the following components:
Midplane—Transports packets, notifications, and other signals between the
FPCs and the Packet Forwarding Engine (as well as other system components).
Physical Interface Card (PIC)—Physically connects the router to fiber-optic
or digital network media. A controller ASIC in each PIC performs control
functions specific to the PIC media type.
Flexible PIC Concentrator (FPC)—Houses PICs and provides shared memory
for processing incoming and outgoing packets. Each FPC hosts four I/O
Manager ASICs, which divide incoming data packets into memory blocks (cells)
before passing them to the SFMs, and reassembles cells into data packets when
the packets are ready for transmission. The FPC also hosts two Packet Director
ASICs—one distributes incoming packets among the I/O Manager ASICs, and
the other distributes outgoing packets to the appropriate PICs on the FPC.
Switching and Forwarding Module (SFM)—Hosts an Internet Processor II ASIC,
which makes forwarding decisions, and two Distributed Buffer Manager ASICs:
one distributes data cells to the shared memory buffers on the FPCs and the
other notifies the FPCs of forwarding decisions for outgoing packets.
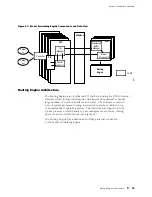
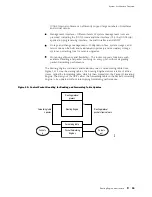
Data Flow through the Packet Forwarding Engine
Use of ASICs promotes efficient movement of data packets through
the system. Packets flow through the Packet Forwarding Engine in
the following sequence (see Figure 23):
1.
Packets arrive at an incoming PIC interface.
2.
The PIC passes the packets to the FPC, where the Packet Director ASIC
distributes them among the I/O Manager ASICs.
3.
The I/O Manager ASICs process the packet headers, divide the packets into
64-byte data cells, and pass the cells through the midplane to the SFMs.
4.
The Distributed Buffer Manager ASICs on the SFMs distribute the data cells
throughout memory buffers located on and shared by all the FPCs.
5.
For each packet, an Internet Processor II ASIC on an SFM performs a route
lookup and decides how to forward the packet.
6.
The Internet Processor II ASIC notifies a Distributed Buffer Manager ASIC of
the forwarding decision, and the Distributed Buffer Manager ASIC forwards the
notification to the FPC that hosts the appropriate outbound interface.
7.
The I/O Manager ASIC on the FPC reassembles data cells in shared memory
into data packets as they are ready for transmission and passes them through
the Packet Director ASIC to the outbound PIC.
8.
The outbound PIC transmits the data packets.
52
Packet Forwarding Engine Architecture
Summary of Contents for Internet Router M160
Page 12: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide xii Table of Contents ...
Page 16: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide xvi List of Figures ...
Page 18: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide xviii List of Tables ...
Page 24: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide xxiv Requesting Support ...
Page 26: ...2 Product Overview ...
Page 30: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 6 Safety Requirements Warnings and Guidelines ...
Page 66: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 42 Cable Management System ...
Page 80: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 56 Routing Engine Architecture ...
Page 82: ...58 Initial Installation ...
Page 104: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 80 Unpacking the Router ...
Page 148: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 124 Configuring the JUNOS Internet Software ...
Page 150: ...126 Hardware Maintenance Replacement and Troubleshooting Procedures ...
Page 242: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 218 Troubleshooting the Power System ...
Page 244: ...220 Appendixes ...
Page 292: ...M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide 268 Packing Components for Shipment ...
Page 301: ...Part 5 Index Index 277 ...
Page 302: ...278 Index ...