12
Id.-Nr.: 1556.212 .1-07
System overview
•
IEC programming: All languages
•
Robot programming: Robot-specific functions can be used (see PLC robotic pro-
gramming manual).
•
Axis interface: Function blocks to control axes directly from the IEC application.
•
Advanced programming: Interface for the programming of motion libraries based
on the axis interface.
•
RC interface: Function blocks to control the robot control from the IEC applica-
tion.
3.3
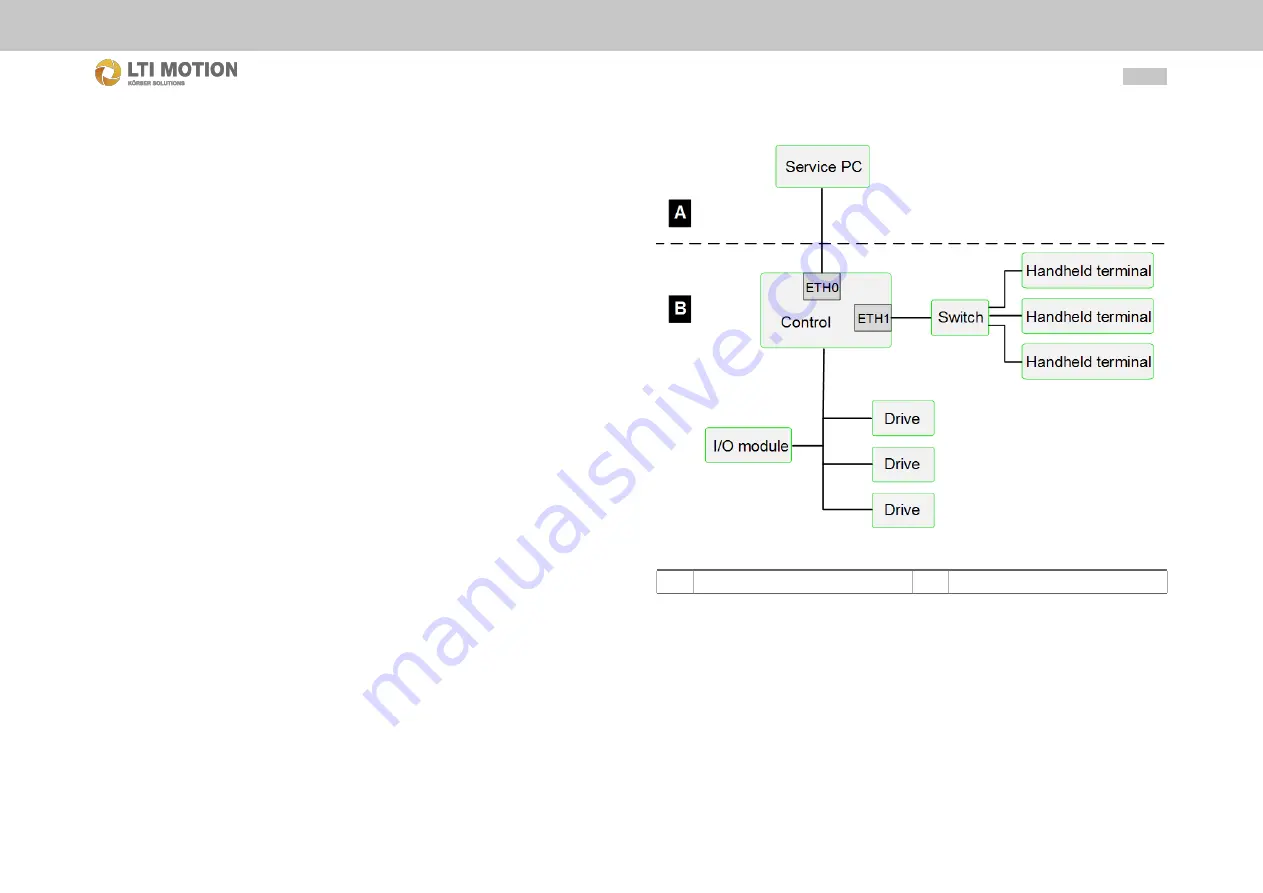
Network design
Typically, the components of the control system are located in their own network (ma-
chine network) that is inaccessible from the outside. The control offers an additional
network connection in order to access the control from a thirdparty network (external
network), e.g. for service work.
Fig. 3.3:
Network design
A
External network
B
Machine network
The IP address of the external network is typically specified by a network administra-
tor. At initial startup of the control with MotionCenterthe IP addresses of the devices
are not attuned with each other. The network settings of the PC or the controls there-
fore must be adjusted.
The communication connection between PC and control can either take place
through a direct connection via a
crossed
Ethernet cable between the Ethernet inter-
face of the PC and the On-board-Ethernet of the control or via a switch.
If a DHCP server exists on the network, the network address can be obtained auto-
matically. If no DHCP server exists, or if there is a direct connection between the con-
trol and the PC, a static network address must be used.













































