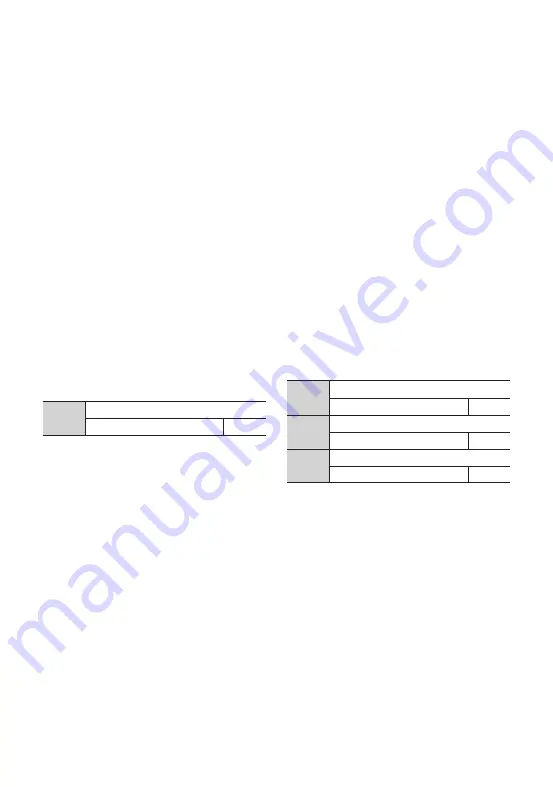
116
0: AI1
PID feedback is given by external analog
signal AI1
1: AI2
PID feedback is given by external analog
signaI A12
2: AI1+AI2
PID feedback is given by AI1 and AI2.
3: AI1-AI2
PID feedback is determined by difference of
AI1 and AI2. When the difference is negative,
the feedback value is 0.
4: MAX {AI1, AI2}
5: MIN {AI1, AI2}
6: pulse setting
7: RS485 communication
F8.04
PID controller advanced setting
0000 ~ 1001
000
LED one's place: PID regulation characteristic
0: positive logic
Positive logic is defined as that when
feedback signal is smaller than PID
input,the driver output frequency should
be decreased (decrease feedback signal) so
as to maintain the balance of PID. Examples
are like tension control of winding, constant
pressure water supply control,etc.
1: negative logic
Negative logic is defined as that when
feedback signal is larger than PID input, the
driver output frequency should be increased
(decrease feedback signal) so as to maintain
the balance of PID. Examples are like
tension control of unwinding, central air-
conditioning control, etc.
LED ten's place: proportion regulation
characteristic (reserved)
0: integral regulation of constant proportion
1: integral regulation of automatically
changing proportion
LED hundred's place: integral control
characteristic
0: stop integral regulation when frequency
arrives at upper/lower limit
1: continue integral regulation when frequency
arrives at upper/lower limit
It is recommended to cancel continuing
integral regulation for system requiring
quick response.
LED thousand's place: reserved
0.00: no derivative regulation
Proportional gain (Kp):
It determines the adjusting strength of
PID regulator. The larger of P, the larger of
adjusting strength. But excessive adjusting
strength will result in fluctuation easily.
When feedback and reference shows
deviation, regulating value that is in
proportion to deviation is output. If the
deviation is constant, the regulating value
is constant. Proportion regulation can
response quickly to the feedback changing,
but can't realize floating control alone. The
larger of the proportional gain, the quicker
F8.05
Proportional gain KP
0.01 ~ 100.00s
2.50
F8.06
Integral time Ti
0.01 ~ 10.00s
0.10
F8.07
Derivative time Td
0.01 ~ 10.00s
0.00
4.2 Detailed Function Description
Summary of Contents for SKI600
Page 3: ......
Page 4: ...88888 Operating Instruction Manual High performance Vector Inverter ...
Page 179: ......
Page 180: ......
















































