COPYRIGHT © 2001 CANON INC.
2000 2000 2000 2000
CANON iR5000i/iR6000i REV.0 JUNE 2001
CHAPTER 2 MAIN CONTROLLER
2-11 S
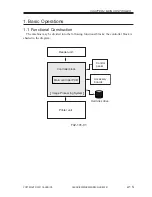
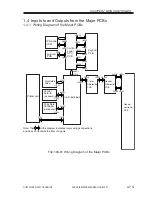
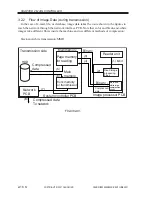
2.3 Controlling the Image Memory
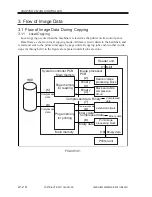
The image data resulting from binary processing is processed as follows:
2.3.1 Compression/Decompression, Rotation, Enlargement/Reduction
Binary data is processed so that the images may be compressed/decompressed (for elec-
tronic sorting), rotated, or enlarged/reduced.
2.3.2 SDRAM
The SDRAM is used to temporarily store the image data held by the image memory.
2.3.3 Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
As opposed to its function as an image server, the box function is made use of to store im-
age data.
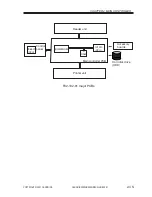
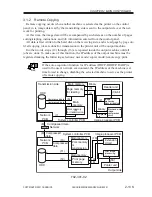
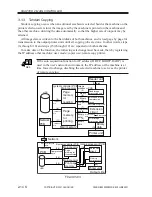
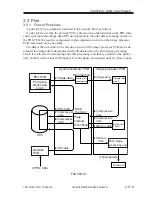
2.4 Output Image Processing
The image data sent to the printer unit is processed as follows:
2.4.1 Smoothing
a. When Outputting Read Images
In the case of text/text photo mode, a 600x600-dpi input image is converted into an im-
age of 1200* × 600 dpi.
In smoothing, the image data is compared against several hundred templates (7×7 pixel
pattern matrixes), and each pixel in question is replaced as needed.
b. When Outputting Printer (PDL) Images
The type of smoothing best suited to PDL is performed while converting 300×300-dpi
or 600×600-dpi data into data of 2400*× 600 dpi.
*Equivalent.
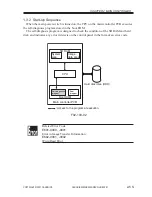
2.4.2 Thickening (PDL output only)
If so specified using the printer driver, thickening (processing) is performed to improve
the reproduction of fine lines.
Lines in a PDL output image are thickened by adding 1/2 pixels (1200 dpi) in horizontal
direction and 1/2 pixels in right vertical direction.
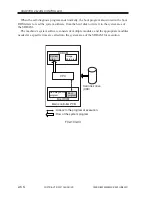
2.4.3 Binary-Binary Density Conversion (read image output only)
This processing is used as an auxiliary function serving as part of density adjustment
while copies are being made.