X90 mobile modules
244
X90 mobile system User's manual V 1.20 - Translation of the original manual
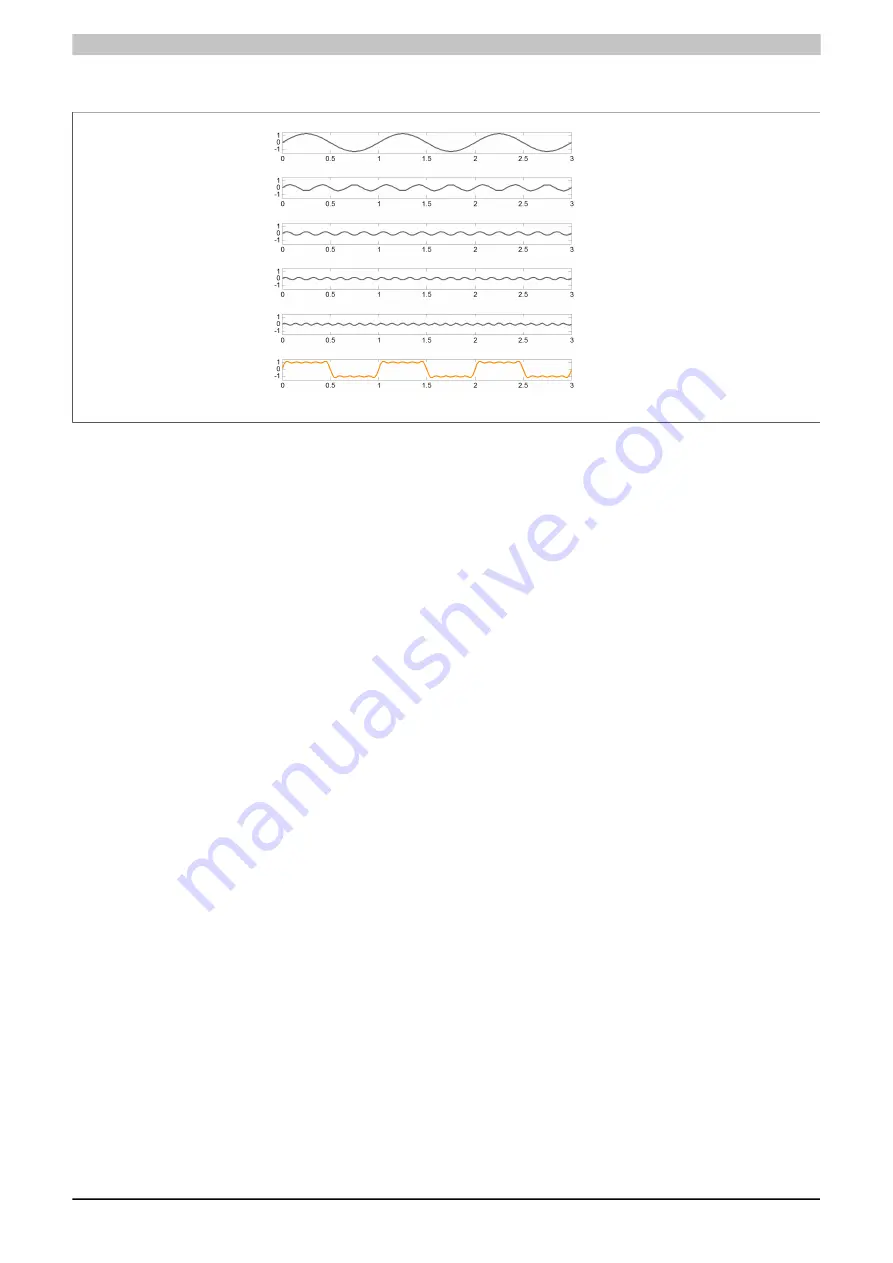
Sinusoidal oscillation with 1 Hz and an amplitude of 1 and sinusoidal oscillations with 3x, 5x, 7x and 9x the base
frequency and a lower amplitude.
Time [s]
Amplitude
Base frequency (GF)
3 x GF
5 x GF
7 x GF
9 x GF
Total
Figure 75: Sinusoidal oscillation with several harmonics
General description
The Fourier transform is the basic principle of frequency analysis. It assumes that each harmonic oscillation can
be broken down into any number of sinusoidal and cosinusoidal waves, the sum of which reproduces the original
oscillation. Linked individual waves are "broken down" again accordingly.
Probably the most well-known concept in connection with signal processing and frequency analysis is the fast
Fourier transform, or FFT.
In order to be able to evaluate single partial oscillations into amplitude and frequency, the digitized time signal is
converted into a frequency spectrum. In addition, a small extract is taken from the signal; this is known as the time
window. Using the FFT algorithm, the frequency spectrum is calculated from this so that each involved oscillation
and its associated frequencies and amplitudes is shown as a single line in the line spectrum.
Example
For a single sine signal with a constant frequency, a single line is shown in the frequency spectrum.
















































