X90 mobile modules
X90 mobile system User's manual V 1.20 - Translation of the original manual
225
Transmitting and receiving with Forward
The basic algorithm for transmitting and receiving data remains the same. With the Forward function, up to 7
unacknowledged sequences can be transmitted. Sequences can be transmitted without having to wait for the
previous message to be acknowledged. Since the delay between writing and response is eliminated, a considerable
amount of additional data can be transferred in the same time window.
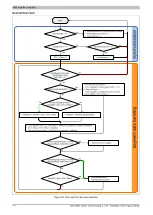
Algorithm for transmitting
Cyclic status query:
- The module monitors OutputSequenceCounter.
0) Cyclic checks:
- The CPU must check OutputSyncAck.
→ If OutputSyncAck = 0: Reset OutputSyncBit and resynchronize the channel.
- The CPU must check whether OutputMTU is enabled.
→ If OutputSequenceCounter > OutputSeque 7, then it is not enabled because the last sequence has not yet been acknowledged.
1) Preparation (create transmit array):
- The CPU must split up the message into valid segments and create the necessary control bytes.
- The CPU must add the segments and control bytes to the transmit array.
2) Transmit:
- The CPU must transfer the current part of the transmit array to OutputMTU.
- The CPU must increase OutputSequenceCounter for the sequence to be accepted by the module.
- The CPU is then permitted to
transmit
in the next bus cycle if the MTU has been enabled.
The module responds since OutputSequenceCounter > OutputSequenceAck:
- The module accepts data from the internal receive buffer and appends it to the end of the internal receive array.
- The module is acknowledged and the currently received value of OutputSequenceCounter is transferred to OutputSequenceAck.
- The module queries the status cyclically again.
3) Completion (acknowledgment):
- The CPU must check OutputSequenceAck cyclically.
→ A sequence is only considered to have been transferred successfully if it has been acknowledged via OutputSequenceAck. In order to detect potential trans-
fer errors in the last sequence as well, it is important to make sure that the algorithm is run through long enough.
Note:
To monitor communication times exactly, the task cycles that have passed since the last increase of OutputSequenceCounter should be counted. In this way,
the number of previous bus cycles necessary for the transfer can be measured. If the monitoring counter exceeds a predefined threshold, then the sequence
can be considered lost (the relationship of bus to task cycle can be influenced by the user so that the threshold value must be determined individually).
Algorithm for receiving
0) Cyclic status query:
- The CPU must monitor InputSequenceCounter.
Cyclic checks:
- The module checks InputSyncAck.
- The module checks if InputMTU for enabling.
→ Enabling criteria: InputSequenceCounter > InputSeque Forward
Preparation:
- The module forms the control bytes / segments and creates the transmit array.
Action:
- The module transfers the current part of the transmit array to the receive buffer.
- The module increases InputSequenceCounter.
- The module waits for a new bus cycle after time from ForwardDelay has expired.
- The module repeats the action if InputMTU is enabled.
1) Receiving (InputSequenceCounter > InputSequenceAck):
- The CPU must apply data from InputMTU and append it to the end of the receive array.
- The CPU must match InputSequenceAck to InputSequenceCounter of the sequence currently being processed.
Completion:
- The module monitors InputSequenceAck.
→ A sequence is only considered to have been transferred successfully if it has been acknowledged via InputSequenceAck.